Before understanding how water pollution threatens the environment, we must understand why water is essential and why we need to stop water pollution for our survival. Water plays an essential role for all cells within the human body – neurons, muscles, organs – as it supplies their needs with essential hydration and energy storage capabilities. Human beings utilize two primary approaches for accessing and using this essential resource: diffusion and aquaporin channels.
Why we should educate about how water pollution affects the environment and how to prevent water pollution
Water is an indispensable substance that provides life with its chemical and physical characteristics, yet despite significant efforts made to manage and treat wastewater properly, worrying levels of pollution have been reported recently. Each year, humans contribute 14 billion pounds of plastic waste into the oceans and release 1.2 trillion gallons of untreated effluent into our water systems, increasing pollution to such an extent that by 2050 47% of people on Earth will struggle to obtain clean drinking water due to increasing levels of contamination. Here we explore its main impacts, along with examples of environmental disasters caused by it.
In lakes and other water bodies, plants and algae grow too much due to the fertilizers used in agriculture. This is because they supply lakes or other aquatic environments with fertilizers from agriculture which results into oxygen deficiency hence less life in them. Sometimes these organisms smother plants or animals, creating dead zones. Occasionally toxins are produced that are harmful to aquatic animals – Klamath River in California suffered an algal bloom during 2017 while Toledo witnessed its worst ever blue-green algae outbreak along the Lake Erie shoreline in 2011.
Let’s find out why you should read this entire article of ours.
Water pollutants can originate from various sources:
- Sewage: The release of untreated human waste and wastewater from cities and towns.
- Industrial Wastewater: The discharge of chemicals and contaminants from factories and manufacturing plants.
- Agricultural Activities: The seepage of chemicals, fertilizers, and pesticides from farms, leads to water contamination.
- Oil Spills: Accidental or intentional release of oil into marine and aquatic environments.
- Marine Debris: The accumulation of plastic waste, debris, and litter in water bodies.
- Stormwater Runoff: The flow of rainwater and melted snow from land into waterways, carrying pollutants with it.
Individuals, communities, and governments can take steps to stop water pollution and protect our water resources:
- Proper Sewage and Wastewater Treatment: Ensuring that sewage and wastewater undergo proper treatment before being discharged into water bodies.
- Reducing Chemical Use in Agriculture: Minimizing the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides on farms to prevent their runoff into water sources.
- Decreasing Reliance on Fossil Fuels: Employing cleaner and renewable energy sources to reduce water pollution caused by the extraction, transportation, and burning of fossil fuels.
- Redirecting Stormwater to Treatment Facilities: Implementing systems to direct stormwater to treatment facilities, where it can be properly filtered and cleaned before being released back into the environment.
- Avoiding Littering: Practicing responsible waste disposal and never littering, as litter can easily find its way into waterways and contribute to pollution.

What Science Teaches Us to Stop Water Pollution
Given people’s increasing concern for environmental sustainability, it is more important than ever to understand how science fights water pollution. Science equips us with everything that we need to know about three types of water pollution: sewage discharge, agricultural drainage runoff and industrial waste products. Such studies have allowed us to examine what may be done by contaminants to humans, aquatic ecosystems as well as the general environment around. Knowledge from science involves not only awareness but also judgment knowledge application grounded on information availability should one need effective understanding solutions derived through scientific investigation (some pleasant moments were experienced when cleaning dirtied rivers). Water will always remain a key resource in any given society hence making it clean should be our top priority.

How can nobody care when millions of websites have published bad news? The inability to do anything has been the heart of American politics for a long time, we worry about everything until we are sick, and what can you do when billionaires control everything? People mostly care about what they think they can achieve – like a job or housing or knowing they won’t die from lack of health insurance another day.
Water — dying fish, oceans full of garbage — is a big problem. But whenever people ask the government to solve problems by providing money through taxes for services that could fix them, nothing happens. I wish every poll question about these problems could be as simple as this: Will you support an international effort to clean our waters and seas?
Let’s take a look at science’s view on water pollution for 2024 and publish those studies here. These are already being talked about in thousands of blogs online – only it took everybody else until now to bring them up. Now it’s their turn; so readers get some 2024 topics while they’re still fresh.
Confined Animal Feeding Operations (CAFOs) and Water Pollution
In Southeast Minnesota and other parts of the country, livestock manure spreading has been associated with water pollution and fish kills. Jeff Broberg, a licensed professional geologist and experienced risk manager, has witnessed the unfortunate consequences of this practice firsthand.
- Case Study: Fish Kills in Western Winona County – Western Winona County near Lewiston has witnessed four fish kills within 10 miles within six years, all occurring during summer when dairy farmers spread animal dung and applied highly toxic fungicides on fields with freshly cut grass, leading to heavy rainstorms that flushed this manure into waterways, depleting oxygen levels, making water murky, and introducing harmful chemicals that are toxic for fish.
- Jeff Broberg made an alarming observation: the lack of compliance with best management practices. For instance, he witnessed a farmer spreading manure directly into a drainage way despite guidelines existing and this practice continues today.
- The Challenge of Manure Storage – Large livestock facilities often lack suitable manure storage solutions, forcing year-round manure application by farmers in an effort to spread as much manure before rainfall occurs and prevent the need for costly cleanup efforts. This often forces them into an arms race against Mother Nature as they work against time to complete this task before it falls under her full force and shear.
- Timing is vital when it comes to producing hay for baling – an agricultural practice that typically involves farmers cutting the crop and leaving it to dry before baling – because farmers typically need five or seven days of dry weather before spreading manure over it. It is recommended that manure be applied within four days after cutting for optimal utilization however, often finding this window of opportunity may prove challenging.
Activities from a group of activists called Lake Erie advocates have taken action by funding billboards in Toledo, Cleveland, and Columbus. These billboards send a clear message, stating “Stop Poisoning Lake Erie” and highlighting that Lake Erie is not a toilet. The group hopes that more people become aware of how factory farms in Point Place impact the environment. Mike Ferner is an activist and former Toledo city councilman living there for four decades now. He attributes Lake Erie’s pollution to factory farms housing pigs, cows, and poultry such facilities produce over five and half million tons of manure per year from these animals alone. Put this into perspective, the amount of phosphorus produced from animal sources equals that produced by all 21 million residents in Ohio, Indiana, Chicago, and Atlanta combined. Concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs), commonly referred to as animal factory farms have seen rapid expansion since 2005 with 775 CAFOs now located within Ohio with 25 million animals being housed within them.


Concentrated animal feeding companies, or CAFOs, have grown very quickly in Ohio. Between 2005 and 2019, the number of CAFOs in the state went up. There are now 775 of them. 25 million animals live in these CAFOs, which is crazy. In Ohio, the Ohio Department of Agriculture is in charge of managing CAFOs. They have set specific limits on the number of animals allowed in each type of operation. The current regulations permit 2,500 swine, 700 dairy cows, 1,000 beef cattle, 82,000 chickens for egg production, and 125,000 chickens bred for consumption
Lead Contamination in Tap Water
We have found a research report detailing recent lead levels in water in Germany which we are presenting here for the convenience of our readers.
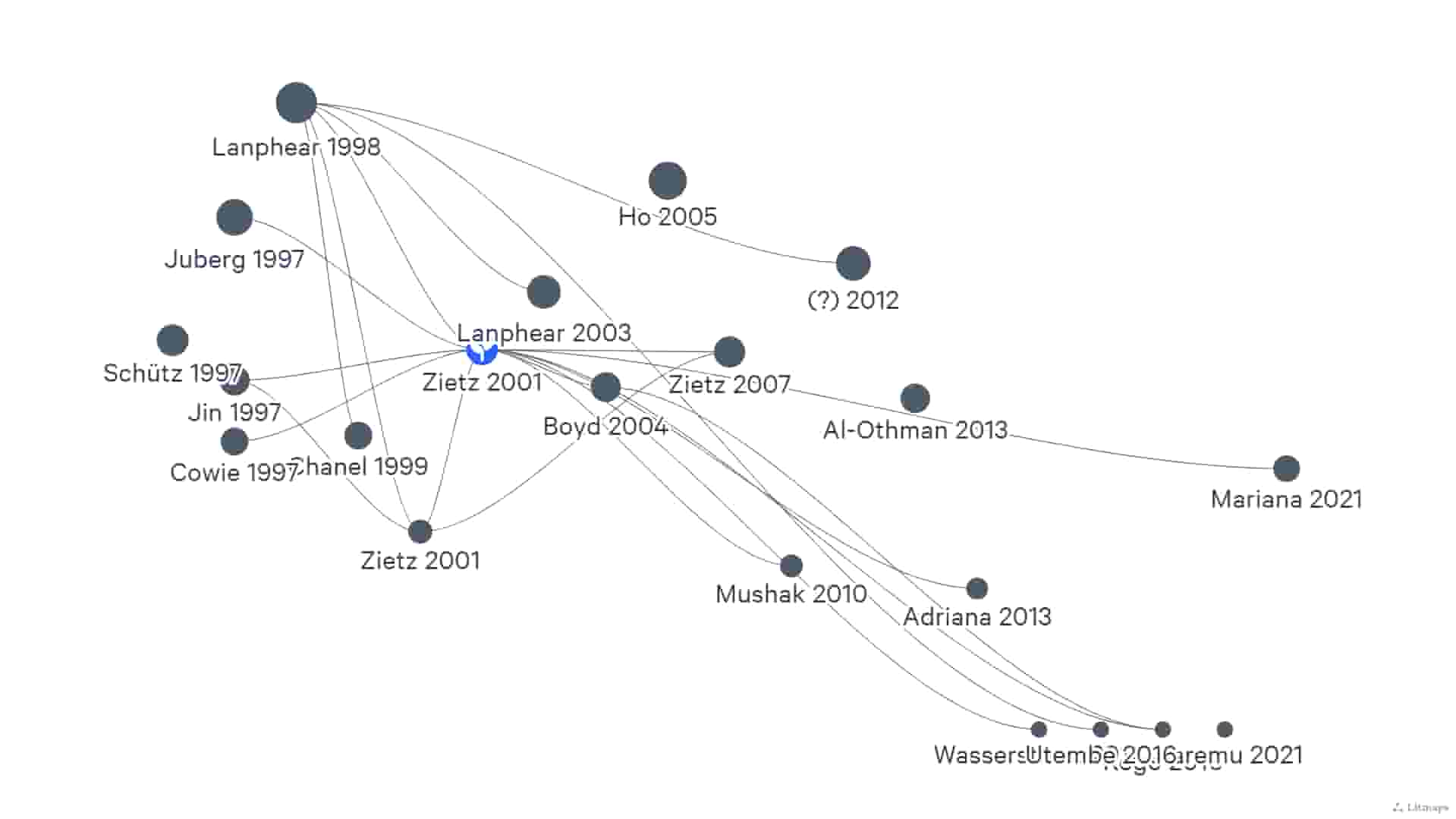
Here this image shows in which states what amount of lead in what year and what testing led to lead capture and the effects against it are mentioned in this recharge data. At this stage, we wanted to see how much lead was found in the water in Chicago and we tried to illustrate this with a diagram.
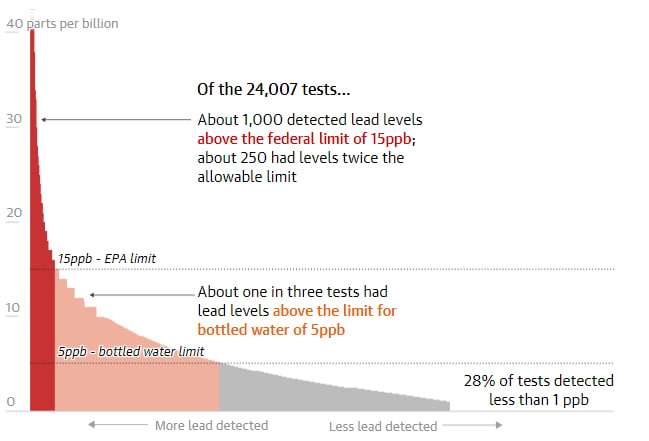
The most alarming level of reporting we’ve come across as we search the entire online world is that US schools are now finding lead in the water, which is turning into deadly life-destroying conditions for young children.
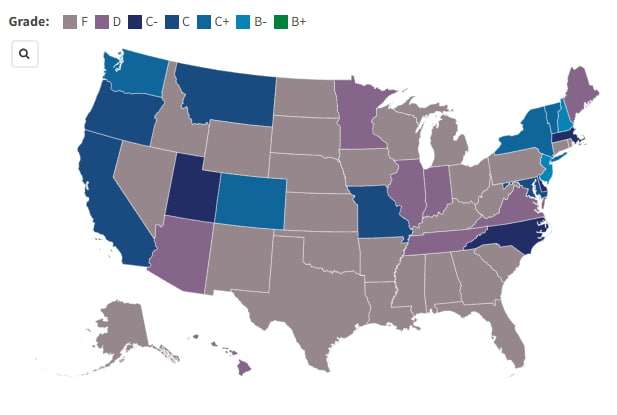
Our writing serves to inform and convince readers to recognize how essential and reasonable it is to prevent water pollution. If saving children is important to you, take action – however small – through us in order to help. Julie from Boston shared her experience after receiving a letter from their elementary school superintendent three years prior, informing them they had tested above the 15 parts per billion lead action level. Precautionary steps were taken, such as switching off all water fountains and providing bottled water as an alternative source. Julie also voiced her concerns for students regarding lead contamination in schools. A study of school drinking water guidelines across 31 states and D.C. has revealed that 22 are failing to protect kids from lead exposure in school drinking water supplies, due to fixtures such as fountains and faucets that contain lead as well as parts that contain it within schools that do not comply. The report attributes these issues to fixtures like fountains or faucets that contain it being the cause.
An Ohio school water fountain had more than 100 times the EPA action level for lead contamination, Chicagoland schools exceeded this figure 212-fold while Massachusetts schools exceeded it almost 1500-fold – raising concerns as to the costs associated with combatting lead poisoning in schools. However, not all solutions require extensive expenses simple measures like installing filters on faucets or fountains used for cooking and drinking may provide a cost-effective means of combatting lead contamination issues in schools. Filters typically cost as little as $100 or even less and thus offer schools another feasible option when faced with lead contamination problems. It should be acknowledged that not every community will be capable of managing lead pollution alone, therefore states and federal governments are encouraged to provide funding assistance so schools can reduce lead contamination levels more easily.
Soil Erosion and Water Quality
Soil erosion is a natural process in which top layers of soil are disturbed or removed due to various forces and can have adverse impacts on agriculture, water quality, and ecosystem health. Soil erosion presents significant environmental concerns that threaten agriculture production as well as overall system functioning and sustainability. Water can be an incredible force that has the power to uproot entire areas in an instant, taking large parts of land with it as it traverses it and carrying off pieces of soil and dirt with it.
Water’s movement through the dirt picks up pieces as it goes. Erosion occurs more rapidly during heavy rainfall or swift water flow. Raindrops play an integral part in soil erosion when raindrops hit the ground they break apart dirt particles making them easier for rainwater to wash away – particularly important if soil particles have become compacted due to compacted or lack of vegetation coverage as their impact on raindrops dislodges them easily from their positions on earth’s surface. Our research from over 240 studies across 38 nations enabled us to ascertain the possible age of soil erosion.
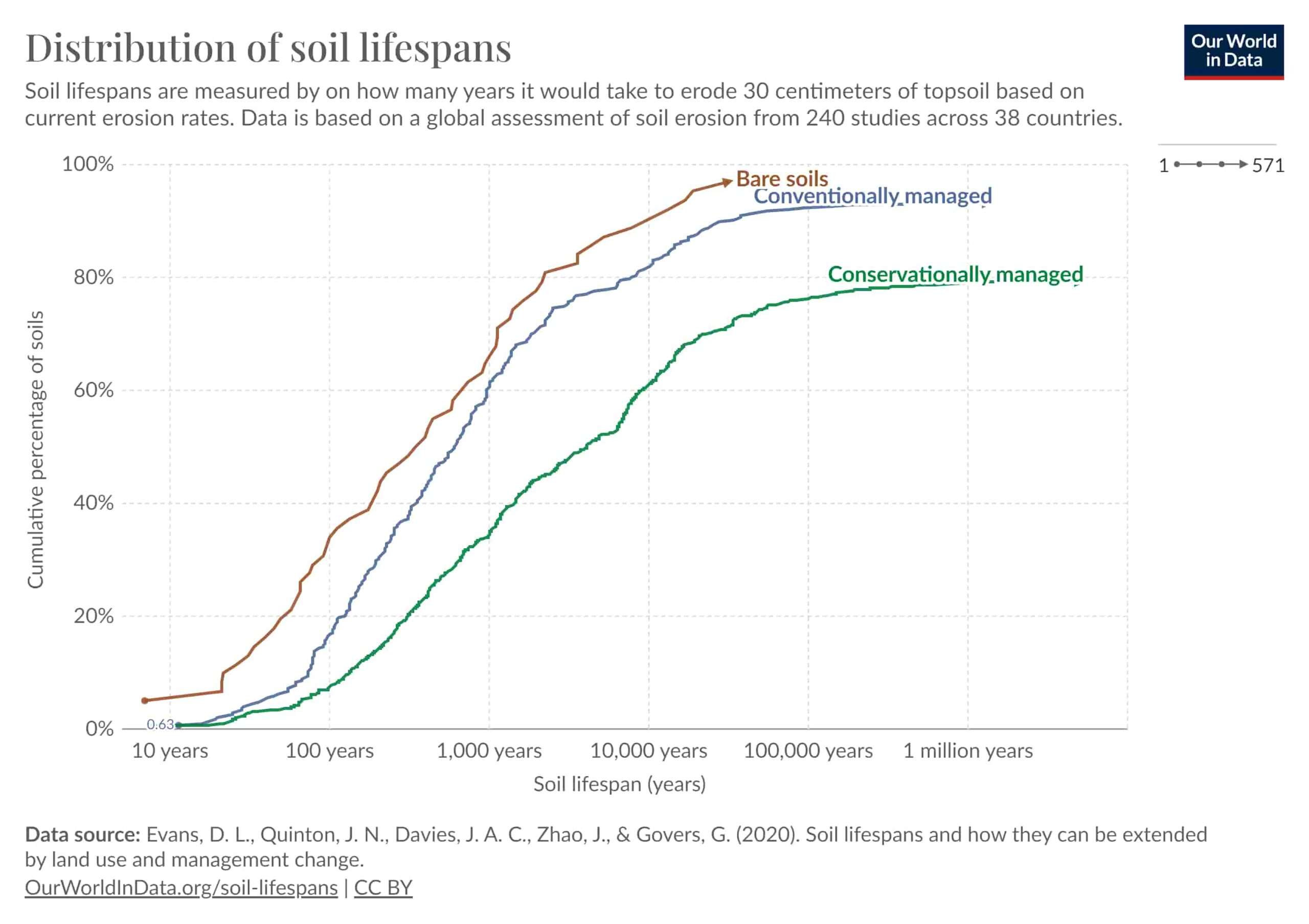
A must-cause effect is also water erosion.
Types are,
- Sheet Erosion
- Rill Erosion
- Ephemeral Erosion
- Gully Erosion
- Streambank Erosion
Safe Drinking Water Act and City Compliance
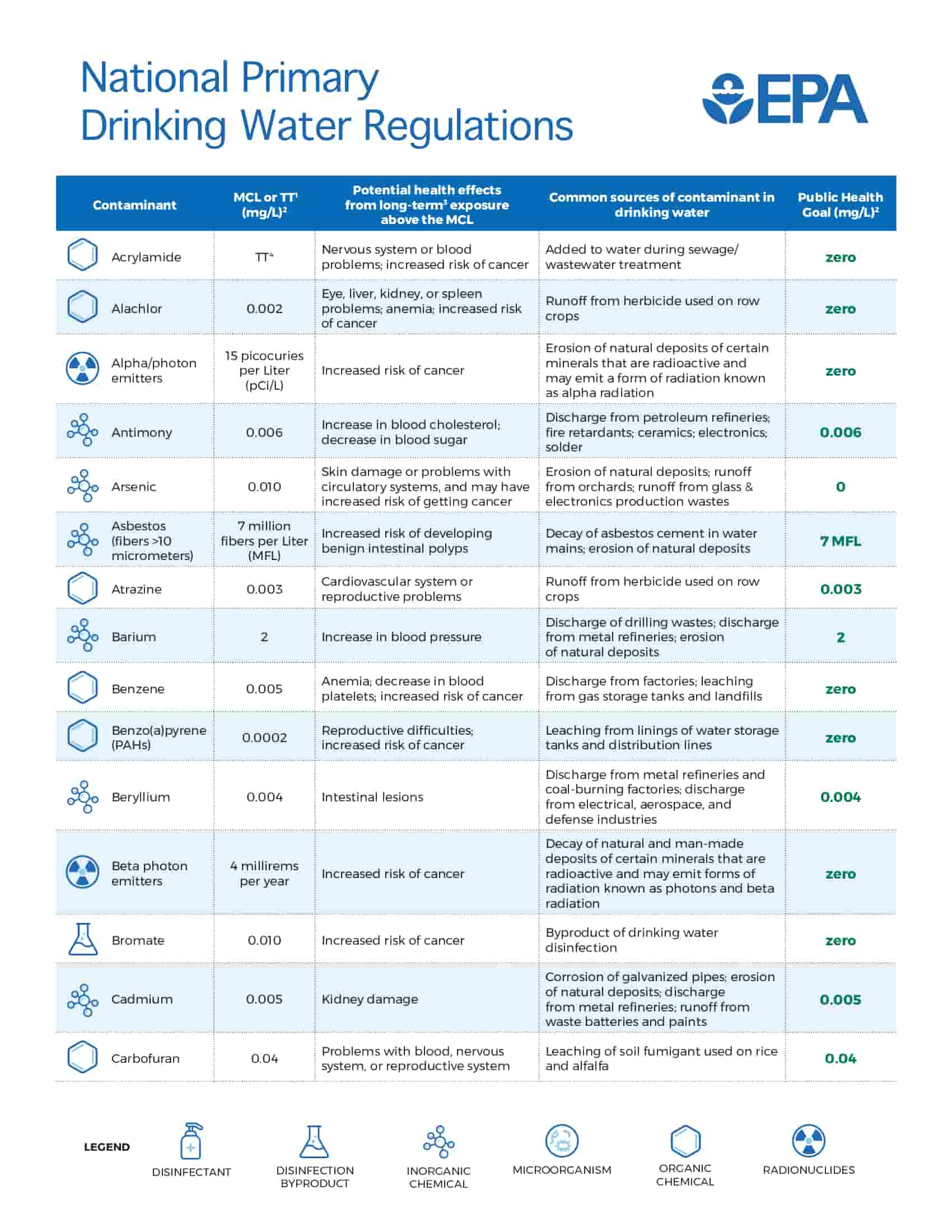
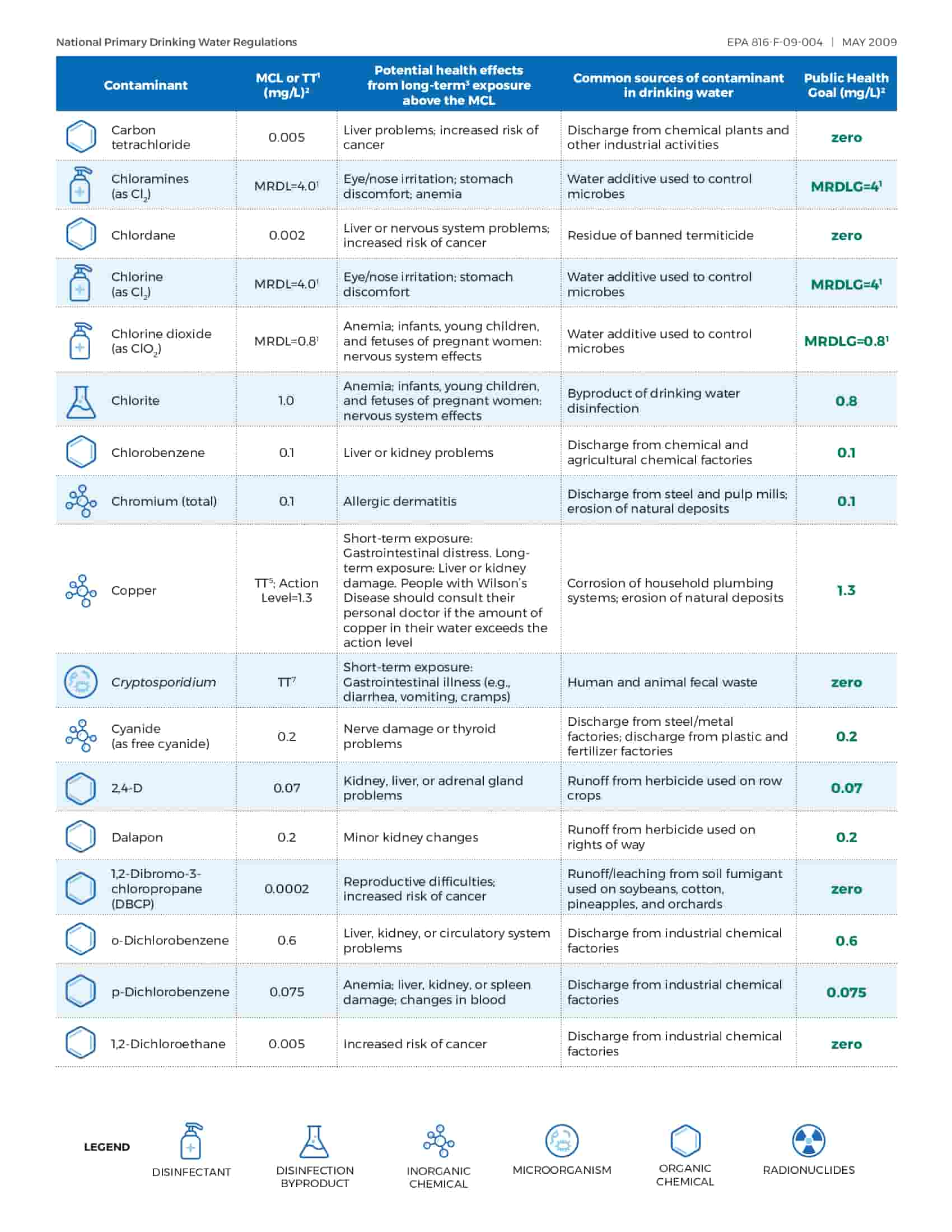
The EPA’s main job is to protect America’s drinking water. The EPA has set safe drinking water guidelines for more than 90 substances. These include drinking water rules that have been made since the Safe Drinking Water Act was changed in 1996 to better protect public health. More than 92% of the people who get their water from neighborhood systems always get drinking water that meets all health standards.
National Primary Drinking Water Regulations,
Water Pollution as a Global Health Timebomb

Water Pollution as a Global Health Timebomb”. Here at our news magazine we decoded it for our readers and provided decoding services as soon as we saw this term from one of the world’s prestigious news magazines, we came across “Water Pollution as a Global Health Timebomb”, we decided to explain to all readers. A modeling study published by Nature Water says by 2100 up to 5.5 billion people or half the global estimated population could have access to dirty open water – signaling an imminent crisis but often ignored: widespread water pollution with severe consequences to all humanity.
Concerns and Threats of Contamination on Aquatic Ecosystems
In 2002, an awful tragedy unfolded on the Klamath River when over 60,000 adult Chinook salmon died during their annual fall run – not alone but alongside coho salmon, green sturgeon, steelhead trout, cutthroat trout, and Klamath small scale sucker species as well. Unfortunately fish kills such as this are becoming an increasingly global phenomenon as temperatures or climate change increase globally – therefore understanding these events’ causes and mitigating future fish kills is paramount in protecting this river and its future salmon runs from further fish kill events occurring elsewhere around the globe to safeguard it for its future success and future fish kill events from occurring elsewhere. Derek Acomb, a Fisheries Biologist with the California Department of Fish and Wildlife, explains that changes in precipitation patterns are playing a significant role. While annual rainfall averages may not be drastically changing, the way rain is distributed throughout the season is. There have been fewer storms of higher intensity recently as such, winter rainy seasons have become longer, with less precipitation falling during fall and spring seasons these changes to precipitation patterns are having direct ramifications on aquatic ecosystems. When left undisturbed, the Klamath River is an influential ecological system. Unfortunately, climate change has already resulted in harmful algal blooms and fish kills due to climate disruption this process of eutrophication begins by increasing levels of nutrients entering waterways.


Let us try to simplify it further, imagine you have a fishbowl filled with happy, swimming fish, plants, and clean water in which to live their lives – now consider what might happen if someone were to add items such as soap or trash into that water source as soon as these contaminants entered it could make its environment unhygienic plants might die, and any remaining inhabitants would feel discontented or even no longer wish to remain there.
The Effects: Environment | US EPA
Imagine for a minute that our large fishbowl (representing rivers and lakes) received too much plant food from farms such as fertilizer for our rivers and lakes too many nutrients can cause too many algae to flourish in the water, leading to what’s known as an algal bloom: an excess of these tiny green organisms living underwater that make the surface seem slimy green, potentially harming fish or even humans who swim or drink the water directly.


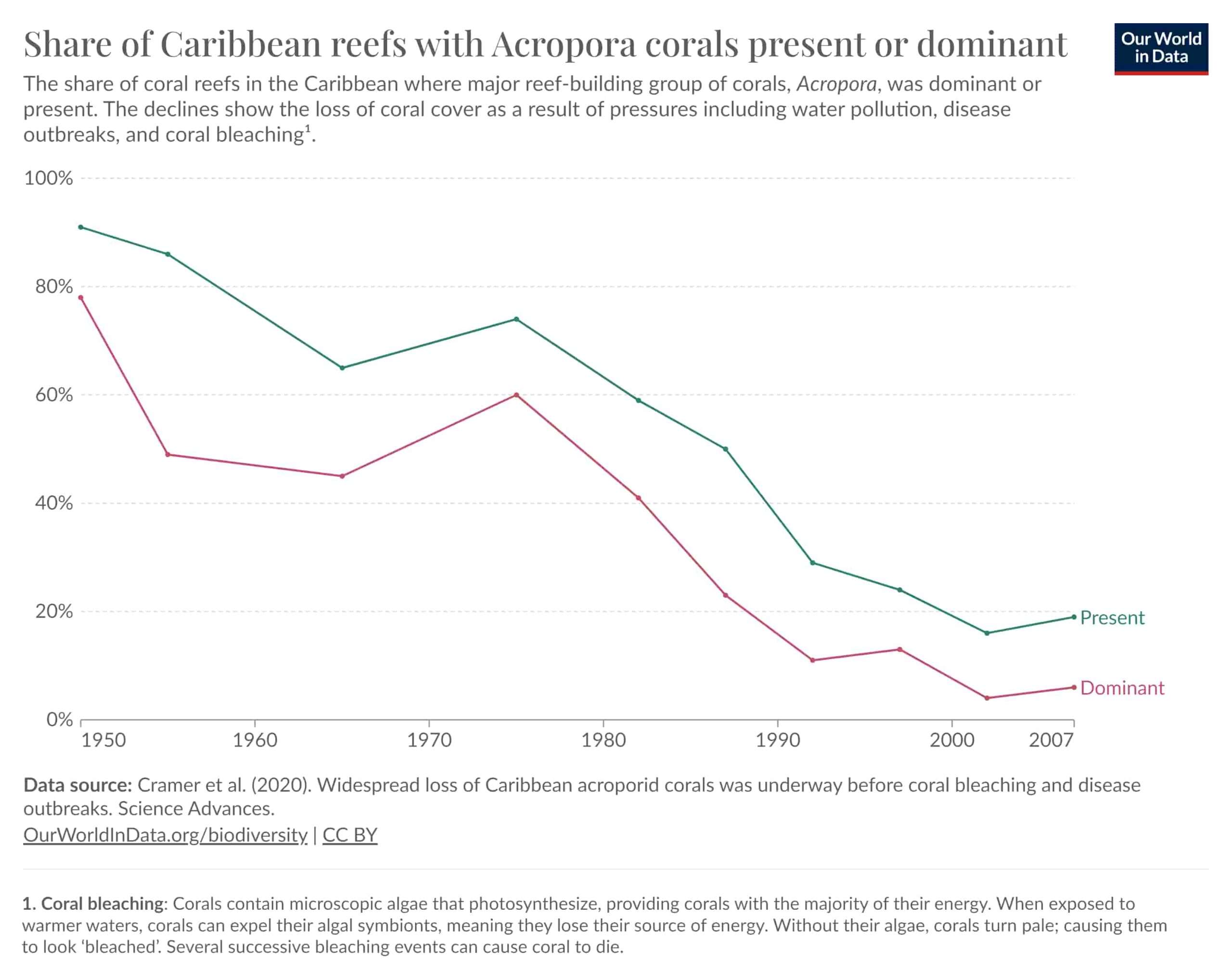
How does pollution impact corals?
Imagine that the ocean is like an enormous, living garden full of coral reefs – like colorful blooms in an actual garden – full of colorful coral flowers called coral reefs that attract an assortment of sea life including fish and creatures such as marine life that make up its ecosystems. When it rains, runoff from fields and cities flows directly into this garden via rainfall sometimes this water may contain harmful substances like chemical cleaners used on cars as well as extra bits of plant nutrition from farms called nutrients.
When this dirty water gets to the sea garden, it can cause trouble for the coral reefs. Here’s what can happen,
- Smothering: The runoff might have tiny bits of dirt and sand that can cover up the corals, kind of like if someone threw a blanket over the flowers in our garden. Corals may not get the sunlight they need to stay healthy if this happens.
- Lower Water Quality: It gets cloudy and full of things that shouldn’t be in the water. This makes it tough for the corals to be happy, just like it would be hard for our garden flowers to grow if we poured dirty water on them.
- Disease: The corals can get sick more easily when the water is polluted. Just like too much junk food can make us sick, pollution can make it easier for corals to catch diseases.
So, NOAA, which is like a group of ocean doctors, tells us that we need to keep our land and water clean. This way, when rain washes into the ocean, it doesn’t bring pollution that can hurt the corals. It’s important to take care of our sea gardens, so all the fish and creatures that live there can stay healthy and happy.

Nonpoint Source: Agriculture | US EPA (Broad Discussion)
EPA research on agricultural nonpoint source pollution provides in-depth coverage on this subject matter, detailing that runoff from agricultural operations can significantly degrade water quality. Rain or irrigation water flows over land or through ground surfaces picking up pollutants generated from farming activities before depositing them in rivers, lakes, and coastal waters. Agriculture nonpoint source pollution includes excess nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus, pesticides and herbicides used for farming operations, sediments from soil erosion, and bacteria from livestock or wildlife grazing the land. Such pollutants can pollute water bodies with algal blooms, dead zones, fish kills or degradation of aquatic habitats causing serious environmental impacts to water bodies across the globe.
As part of its effort to address agricultural nonpoint source pollution, the Environmental Protection Agency has advocated the implementation of conservation practices designed to more efficiently utilize fertilizers and pesticides prevent soil erosion manage animal waste more effectively, and manage animal waste more responsibly – these strategies help decrease pollution entering waterways. For this reason, the EPA offers technical guidance and reference documents for state, local, and tribal governments on controlling nonpoint source pollution from agriculture by way of measures such as nutrient management plans, conservation tillage, or buffer zones (riparian buffer zones).
Section 319 grants are another critical tool used by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in their quest to enhance and protect American waters from nonpoint source pollution. They support projects focused on watershed restoration to address impaired areas while simultaneously safeguarding unimpaired ones demonstration and groundwater projects as well as innovative technology demonstration efforts. An effective solution for this form of pollution requires collaboration among various stakeholders farmers, communities, and government agencies alike so as to safeguard and enhance water quality for future generations.




Ocean pollution and marine debris
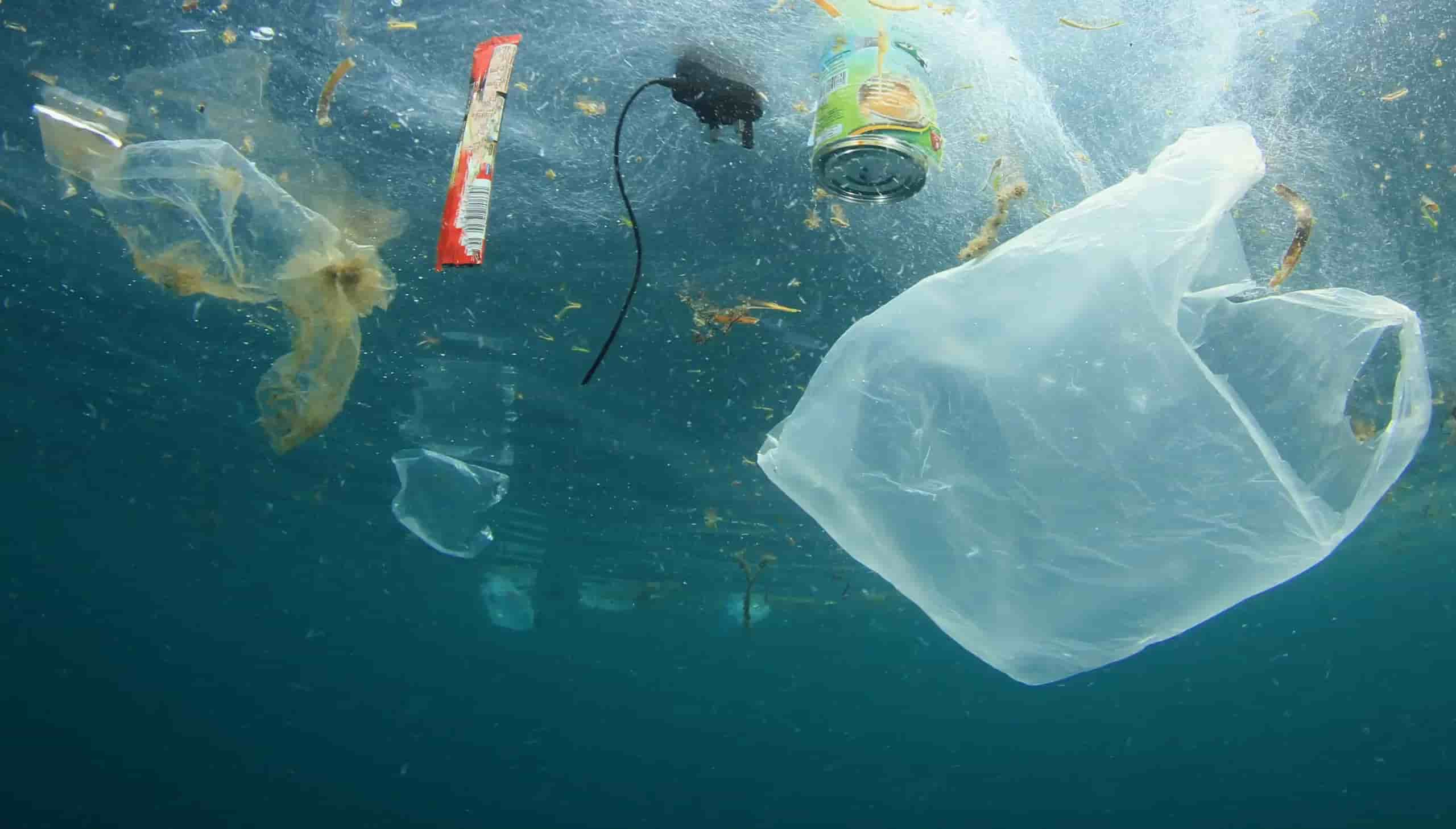
Ocean pollution and marine debris are major environmental problems threatening marine life and ecosystems. Educational materials from various organizations demonstrate how trash such as plastics, metals, rubber, and other materials enters the sea to be harmful large amounts of algae that sink and decompose are one of the main contributors to ocean pollution this process often leaves oxygen levels depleted resulting in low oxygen zones or “dead zones”, where marine life cannot survive (NOAA Ocean Pollution). NOAA Marine Waste Program educates students and the general public on marine debris through lesson plans and other tools, emphasizing its effect on marine animals and ecosystems and supporting projects to study its harmful consequences. The NOAA Marine Waste Program supports projects that seek to investigate or mitigate its adverse consequences by supporting projects designed to investigate or alleviate them (NOAA Marine Debris Program). Educational resources designed for various age groups provide lessons, activities, and curricula designed to teach about ocean gyres and their focus on marine debris accumulation additionally, they compare current data regarding ocean pollution research. These resources aim to raise awareness and foster actions to mitigate marine pollution and preserve aquatic environments.




Soil and water pollution and human health
Imagine our planet as an enormous, lush garden connected by air, water, and land, all parts are interdependent – humans along with plants and animals call this garden home. Now if we throw harmful material like oil into its waters or scatter invisible bits of plastic (called nanoplastics) onto its surfaces then its soil becomes polluted and filthy and starts becoming sickening to all that inhabits it – things quickly get dirty and sickening for all concerned making our home planet unfit to sustain life on it’s precious life support systems.
As soon as our garden becomes sick, so too do we, since we drink and breathe air from it. Cardiologists specialize in protecting hearts. Pollution should be addressed as our polluted gardens pose serious heart and lung risks and make work much harder – therefore keeping it clean for both ourselves and the garden’s sake can keep everyone feeling their best and keeping everyone feeling good. Contamination refers to the unintentional introduction of disease germs or toxic materials into drinking water or edible products, making them unsuitable for consumption and potentially hazardous for health reasons. Contamination occurs when bacteria or harmful compounds infiltrate water sources and render them unsafe to drink.
As such, having efficient sewage systems installed to combat leakage or seepage is absolutely crucial for protecting water resources, and human activities such as defecation or urinating near lakes, rivers, or ponds can contribute to its contamination. By engaging in these practices, germs that cause disease enter the water supply, making it unsafe to drink. Animal waste disposal from dairies or poultries directly into bodies of water also contributes to water contamination. These wastes contain harmful germs, potentially polluting water sources with bacteria like anthrax – making drinking it unsafe and making you sick. Tannery waste can also become a significant water pollutant. Pathogens like E. Coli can lead to serious health risks when consumed or exposed. Pesticides like DDT are another major water pollution threat that disrupts hormonal balance and increases cancer risks when released into our water supplies.

Sociodemographic Disparities in Water Pollution Exposure
Think of clean water like a box of crayons: some are short and used, while others look crisp and brand-new. But what if everyone really needed those new crayons for coloring, and there were only a few new ones among the many that were newer and better? Some kids always get old ones anyway; instead of giving them what they deserve like us with staying clean, drinking, or cooking, we give them used water which is dirty. We need it for general cleanliness too because some tight housing communities have no option but to use unsanitary sources such as rivers which flow from military fire training areas airports etc. where factories emitting PFASs do not evenly cover these towns’ supply.
Sometimes scientists try to find out how often different groups experience this problem – people living in low income areas or with less money – so that all can have new crayons i.e clean water everywhere they want fairness all around nobody should have to use dirty water if they don’t want to. Recently Harvard published a study called “Sociodemographic Factors Are Associated With Abundant PFAS Sources And Detection In US Community Water Systems” asking Americans about their exposure to PFASs across the United States. 18 states provided data on 7873 CWSs who were analyzed by researchers showing links between occurrence of PFASs within drinking systems due to sources. However one notable discovery was made: colored communities are more vulnerable than white communities when it comes down to contamination of PFASs especially through supplies serving high numbers blacks hispanic etc. individuals because rivers which act as source also airports don’t emit equal amount pfas.
Impact of ‘Forever Chemicals’ on Freshwater Fish
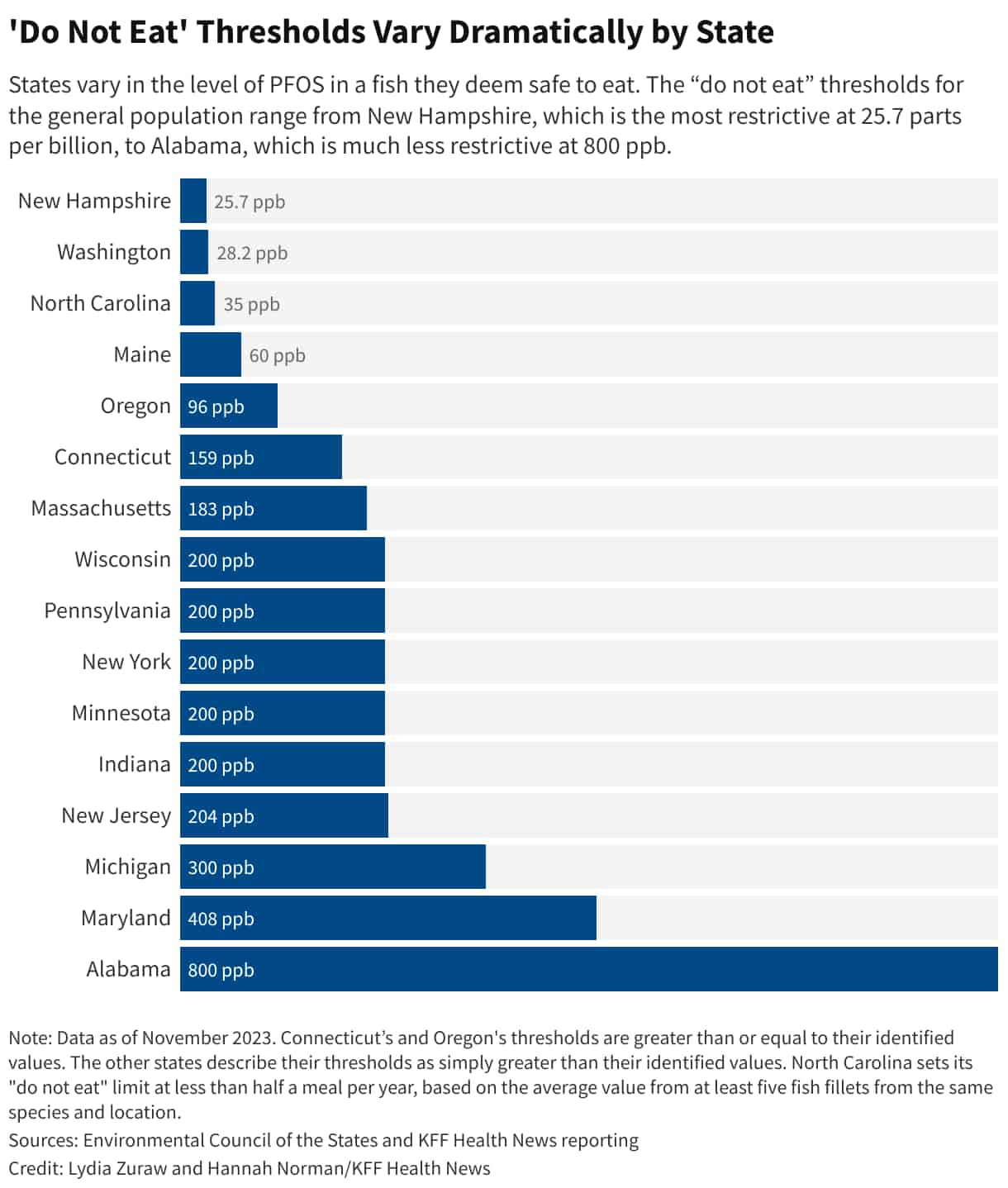
Concerns over the presence of dangerous poisons have increased over time. This issue extends into our rivers and lakes, where fish have been found with high levels of toxic substances. According to KFF Health’s new report on river pollution across America – such as the Catawba River in North Carolina – “forever chemicals” can be found throughout.
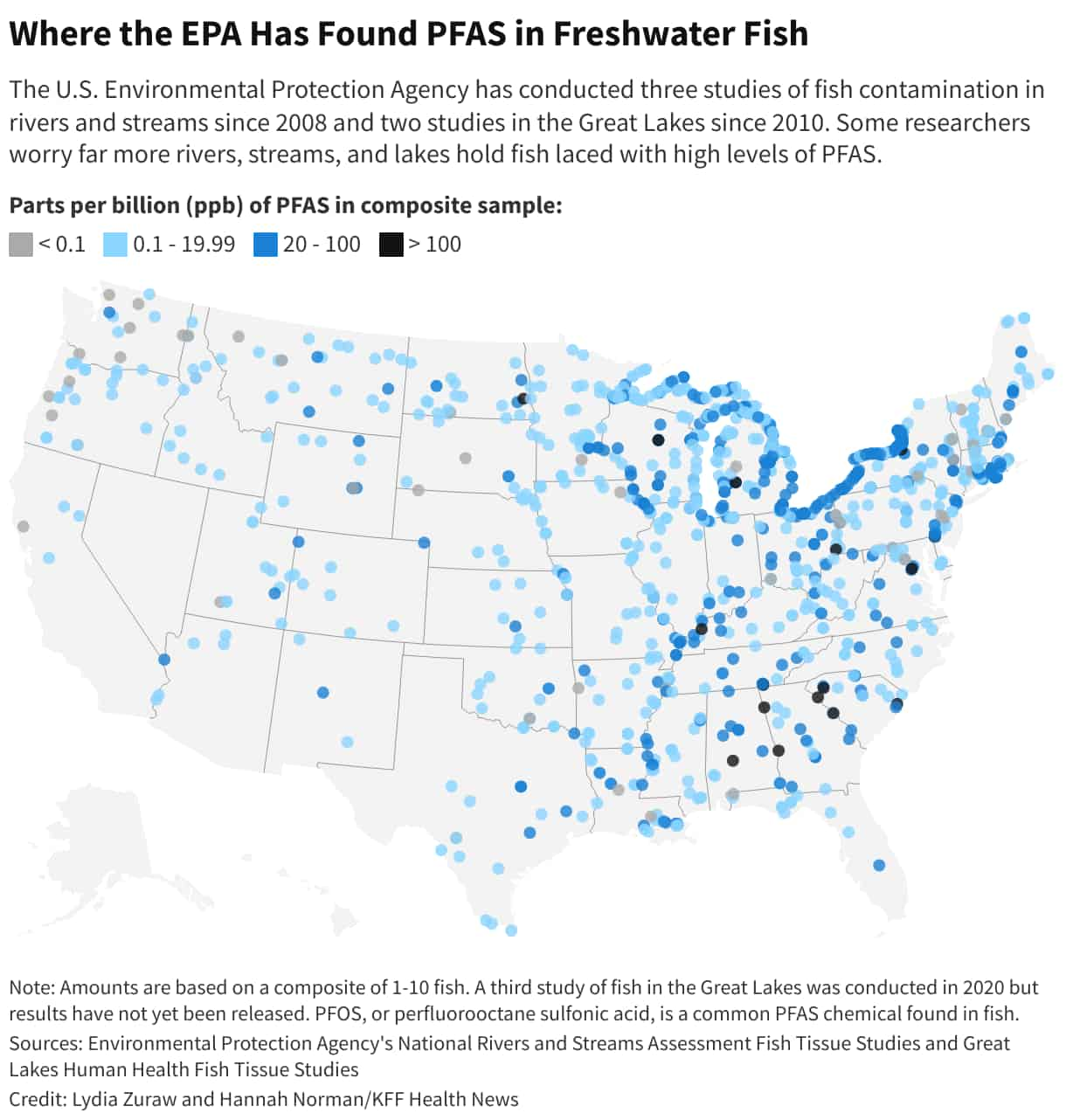
“Forever chemicals” are a group of man-made chemicals called per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Because they don’t react with water or heat, these chemicals are used in a wide range of market and commercial goods. However, they stay in the environment for a long time and can build up in live things, like fish.
About 10 years ago, North Carolina conducted a study that revealed catfish from Catawba River contained dangerously high concentrations of persistent chemicals that cause harm over time. This discovery raised concerns among both residents and fishermen who frequent the river. Jeff Rudisill expressed his discontent at this finding by declaring, “I don’t want my kids eating it” These long-lasting chemicals can have detrimental impacts on fishing activity in areas where they occur once popular spots for catching and cooking fish such as Catawba River have become no longer a safe food source eating contaminated seafood could raise cholesterol, weaken immune systems or even increase cancer risks significantly.

As reported by KFF Health, many states, including North Carolina, fail to adequately inform residents about the presence of forever chemicals in freshwater fish. Only 17 states currently provide notifications on this matter. Studies have linked contamination of rivers and lakes by forever chemicals to various sources including manufacturing facilities and landfills which release toxins into surface waters that eventually reach fish and aquatic organisms.
Groundwater Contamination Sources and Effects
Imagine our soil as being like a sponge that holds water. This water, known as groundwater, can then be used for drinking, bathing, and watering plants. Therefore, its importance cannot be overstated.
However, oil, paint, or even garbage can find their way into the ground through negligent human action – when people allow these items to spill onto the ground or dispose of them inappropriately. When it rains, rainwater carries this trash further underground, much like how a sponge absorbs liquid when you pour juice onto it. Once pollutant-laden material contaminates groundwater, it becomes unsuitable for human use – effectively making it unsafe to drink it and potentially posing health risks to animals and humans alike. We call this “groundwater contamination”, and it has the power to make animals sick as well as people ill.
Maintaining clean groundwater requires us to be mindful of what goes into the ground and how we dispose of waste products, keeping our underground sponge as uncontaminated as possible and consequently our groundwater source clean as well. South Australia boasts a distinguished manufacturing tradition, with industries contributing greatly to its development. Unfortunately, however, decades of indiscriminate chemical use have caused soil and groundwater contamination issues across the region.
Water Contamination Disasters
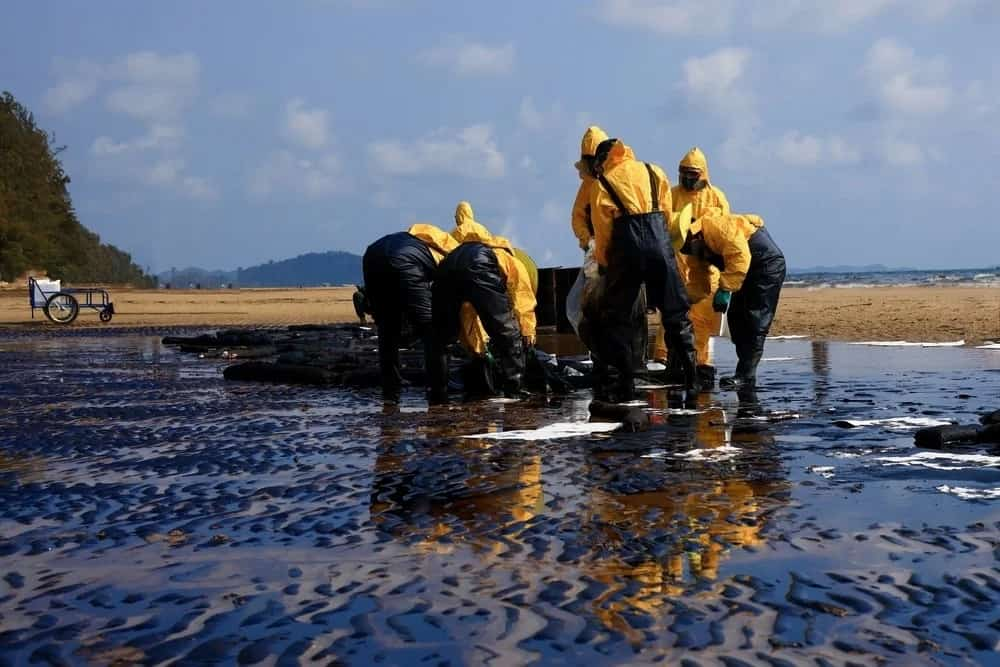
Have you ever given much thought to what might be lurking in your glass of water, invisible threats that could have grave repercussions for your health? While the thought can be unnerving, its relevance cannot be overlooked given the prevalence of water contamination around the globe. Water contamination is a complex issue with numerous causes that are interrelated. Like an intricate web, every thread contributes to creating this overall issue one such cause being industrial waste. Factories and manufacturing plants generate vast quantities of chemicals and waste materials that, when mismanaged, can leak into water supplies and create a hazardous mixture for both people and the environment. Human waste can also play a significant role in water contamination.
Pesticides, fertilizers, and manure used in farming can wash into rivers and streams, polluting them with harmful nitrates and chemicals. Natural disasters like flooding hurricanes or earthquakes may disrupt water supply systems resulting in contamination of our drinking water sources and afterwards, it’s often common for environmental contaminants or damaged infrastructure to leak into it resulting in further contamination.
How to prevent water pollution
Alright, imagine water is like a big, clean bathtub that animals and plants live in. We want to keep it clean so they can be healthy and happy. But sometimes, people put dirty things into the water, like trash, chemicals from factories, or soap from washing cars, which is like making the bathtub dirty. Here’s how we can keep the water clean:
- Don’t throw trash in the water: Always throw your trash in the garbage can, not in rivers, lakes, or oceans.
- Use less plastic: Plastic can end up in the water and hurt the animals, so try to use things that aren’t made of plastic.
- Be careful with chemicals: When grown-ups use chemicals, like cleaners or paints, they should make sure they don’t get into the water.
- Save water: When you use less water for things like brushing your teeth or taking a bath, there’s less dirty water going down the drain.
- Tell others: Teach your friends and family to be good to water, too.
By doing these things, we can help keep the water clean for the fish, ducks, and all the other creatures that live in it. This time we are going to break some more detailed facts about how to prevent water pollution. Be with us, hopefully, no one covered this topic altogether by far.
- Promote Biofiltration Systems – Biofiltration is an environmentally friendly means of purifying water. A biofilter acts like an aquarium full of plants and soil layers for effective cleansing of polluted waters. As water passes through these layers, pollutants are efficiently removed, creating cleaner water suitable for various uses. A biofilter serves as an invaluable resource in water pollution control at its core, it resembles an ordinary garden bed. However, its components are carefully chosen and assembled to maximize pollution removal.
- Advocate for Phytoremediation – Pollutants, contaminants, and toxins might not immediately come to mind when discussing plants but did you know they can play an integral part in the remediation of heavy metals, excess nutrients, petroleum by-products, and pesticides found in our soil? This process is known as phytoremediation. Plants are well known for their photosynthesis ability to transform nutrients from soil, water, and sunlight into energy for use by cells in their tissues.

- Support Wetland Restoration – Wetlands are essential ecosystems, providing many important benefits such as flood control, improved water quality, and wildlife habitat. Unfortunately, their numbers have been steadily decreasing due to human activities like development, agriculture, and pollution. Restoring wetland areas is essential in mitigating human-caused damage while safeguarding these vital ecosystems for future generations.
- Flood Control
- Water Quality Improvement
- Wildlife Habitat
- Economic Benefits
- Implement Rainwater Harvesting – About two-thirds of Earth’s surface is covered by water, though only a very limited portion can be utilized by humanity. With growing populations and industries needing large quantities of it for use and agricultural practices using more of it every year than previously available water is diminishing rapidly. Conserving our water resources requires a range of strategies. One important preventive measure for conservation is rainwater harvesting this method collects and stores rainwater for future use. Rainwater harvesting systems collect, divert, and store rainwater that falls on rooftops, land surfaces, or other locations, in order to use it for irrigation, gardening, domestic purposes or even drinking.
- Promote Sustainable Farming Practices – When it comes to improving sustainability on a farm or ranch, no single solution fits all situations. There are however common practices used by farmers and ranchers throughout the United States to increase profitability, quality of life, and environmental stewardship. Farm and ranch operators who prioritize sustainability aim to produce enough food, fuel, and fiber for today without jeopardizing future production capabilities. Each farm and ranch may take different approaches but the overall vision remains the same. Farm and ranch operations that aim for sustainability consider themselves holistic systems, seeking ways to increase overall health and resilience through constant improvements. Sustainable practices should meet four criteria – productivity, profitability, natural resource enhancement, and improving the quality of life for residents – but for sustainable success to occur, they need four additional things besides these four criteria if success is to be realized.
- Use Eco-friendly Household Products – Single-use plastics are ubiquitous today, contributing to environmental pollution and harming our planet. There are simple and unique sustainable strategies you can adopt at home to lessen this wasteful practice. The Green Jar in Toronto is leading this initiative and offers refillery refilling products with which you can make an impactful difference – see some of their fantastic sustainable swaps.
- Dish Soap Bar
- Vegetable-Based Sponges
- Reusable Coffee Filter
- Repurposing Mason Jars
- Wool Dryer Balls
- Bamboo Toothbrush
- Toothpaste Tablets
- Vegan Dental Floss
- Shampoo Bars
- Stainless Steel Safety Razor
- Bamboo and Cotton Makeup Remover Pads
- Encourage Proper Medication Disposal – Unused medicines pose serious danger if not discarded properly. They could endanger individuals if taken by someone for whom they weren’t intended or accidentally inhaled by children or animals, or cause severe injury if used incorrectly – potentially even leading to danger or death if misused or not taken as directed. It is vitally important that we are aware of their potential risks, and take measures necessary for their safe disposal – they could be hidden anywhere within your home in bathrooms, kitchens, bedrooms, or purses.
- Drug Take-Back Locations
- The FDA’s Flush List
- Disposing in the Trash




- Support Green Infrastructure – As urban areas continue to expand, finding innovative solutions that balance development with environmental preservation has become an ever-more urgent priority. That is where green infrastructure comes into play. Green infrastructure refers to the strategic use of nature’s various capabilities for urban development purposes. Green infrastructure refers to integrating elements like forests, rivers, farmland, parks, green roofs, and walls into city designs and planning processes in order to harness nature’s capabilities and reap its many rewards. By tapping into nature’s capabilities to benefit cities and regions alike, green infrastructure provides many advantages. One of the main benefits is effective forest management, which leads to increased biodiversity and can prevent natural disasters. Furthermore, reusing thin wood from forests helps promote resource circulation for a more sustainable ecosystem. Climate change has brought with it heavy rains and flooding that are becoming increasingly frequent in urban areas. Paved surfaces make absorbing rainfall difficult, leading to waterlogging and damage to green infrastructure provides a solution by tapping into the local environment and terrain to provide relief.
- Educate on Proper Pet Waste Disposal – Have you ever considered what happens to pet waste left lying around the backyard? You might be shocked to learn that, whenever it rains, pet waste and other pollutants end up washing into storm drains which empty into streams and other bodies of water without ever receiving treatment or disposal. Pet waste poses a grave danger to both human health and wildlife alike, containing bacteria and other pathogens which are dangerously contagious when this waste enters our waterways it poses a significant health threat to both people and wildlife alike. Swimming or fishing in polluted waters can result in gastroenteritis, skin infections, and respiratory ailments for swimmers or fishermen while disrupting delicate ecosystems – potentially leading to the extinction of certain species. Contrary to popular belief, pet waste does not make an effective fertilizer. Dog waste in particular tends to be significantly more acidic than other forms of animal excrement and has even been known to kill grass instead of feeding it. When left on lawns for too long, pet waste can create unsightly brown patches with unpleasant odors that create unsightly brown patches with unsightly brown patches as a result. Proper disposal of pet waste is key to maintaining a beautiful lawn.
- Promote the Installation of Greywater Systems – Drought and climate change have become realities that we all must confront. Water shortages have become more frequent, making it essential that we find ways to conserve the limited supply available to us – with greywater reuse becoming an increasingly popular strategy. Greywater refers to any wastewater produced in our homes that does not originate in our toilets and is used for activities other than toileting, such as watering plants and gardens. When used properly, greywater can help us reduce our dependence on freshwater for activities like these – it provides an efficient alternative source of irrigation water.
- Highlight the Importance of Conservation Buffers – Farm waste cleaners use organic filters to filter dirt, nutrients, pesticides, germs, and other pollutants out before they enter rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water. Their filters can remove between 50-80% of nutrients and 60% of sediments – helping keep rivers, lakes, and streams cleaner by stopping harmful things like algal blooms that create pollution problems downstream.

- Advocate for Community Clean-up Events – Step one in organizing a clean-up effort should be to identify an area that could use some attention. Keep an eye out for places with general waste bins or recycling bins for litter disposal, consider suitable meeting points as well. Before embarking on any clean-up activity, it is vital to obtain approval from all relevant authorities and landowners to ensure an efficient process. Should special circumstances arise that prevent cleaning activities from proceeding as scheduled, suspend cleaning to accommodate those needs. Once you have identified and secured permissions for an area, it’s time to build your community. Reach out to family, friends, colleagues, neighbors, and anyone else who might be interested in participating – together we can make a greater difference if more people get involved. Working together, we can unite more people behind our cause of protecting the earth. On the day of your clean-up event, gather your group and hold an initial briefing.
- Push for Industrial Water Treatment Innovations – Water is an invaluable resource that we rely on every day, from breakfast newspaper production to taking a refreshing shower at night, it forms an integral part of life. Unsettlingly, over 80% of wastewater worldwide goes untreated or corrected and this poses an alarming risk to both human health and the environment. A typical individual consumes large volumes of water daily. Water is essential to our everyday lives for drinking, cooking, cleaning, and personal hygiene needs alike. Unfortunately, however, the wastewater we generate must first be properly treated before being returned to the environment. Neglecting wastewater treatment can have disastrous results, including polluted water bodies and the spread of disease-carrying organisms. One innovative solution for wastewater treatment is iMETland’s zero-energy operation investment model. iMETland utilizes electroactive bacteria to purify wastewater, creating a sustainable cycle that connects water, energy, and land resources. This innovative solution not only ensures the responsible use of water but also addresses an essential question about what to do with our daily production of wastewater. Beginning by collecting wastewater from each household in a septic tank, this purification system then feeds its way to a biofilter where electroactive bacteria and electroconductive materials work to purify it further. Remarkably, this purification method can handle up to 25,000 liters per day making it suitable for small communities.
- Encourage the Adoption of Integrated Pest Management (IPM) – Integrated Pest Management (IPM) offers one effective approach to protecting planted forests from pests and diseases while guaranteeing productivity IPM brings together various techniques, divided into phases, to provide an all-inclusive protection plan. By combining various approaches together, Integrated Pest Management ensures responsible yet sustainable control of pests without harming human health or the environment. We will see some phases in this regard,
- Phase 1: Planning and Planting
- Phase 2: Monitoring
- Phase 3: Decision Making
- Phase 4: Efficiency Check
- Promote the Use of Natural Fertilizers – We could go into full detail if we wanted to but we’re going to highlight some of the main reasons here,
- Sustainability and caring for the environment.
- Providing financial help to farms and rural areas.
- Improve the structure, nutrients, and ability of the earth to hold water to improve its health.
- Release nutrients more slowly over longer periods of time. This lowers the amount of nutrients that are lost through leaching.
- Help the ecosystem and variety of the land.
- Lessen the chance of burning plant roots from too much fertilizer.
- Less damage to the environment less waste of nutrients and fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
- All around it is safe for people, animals, and the environment.
- Can be made in the area, creating job chances.
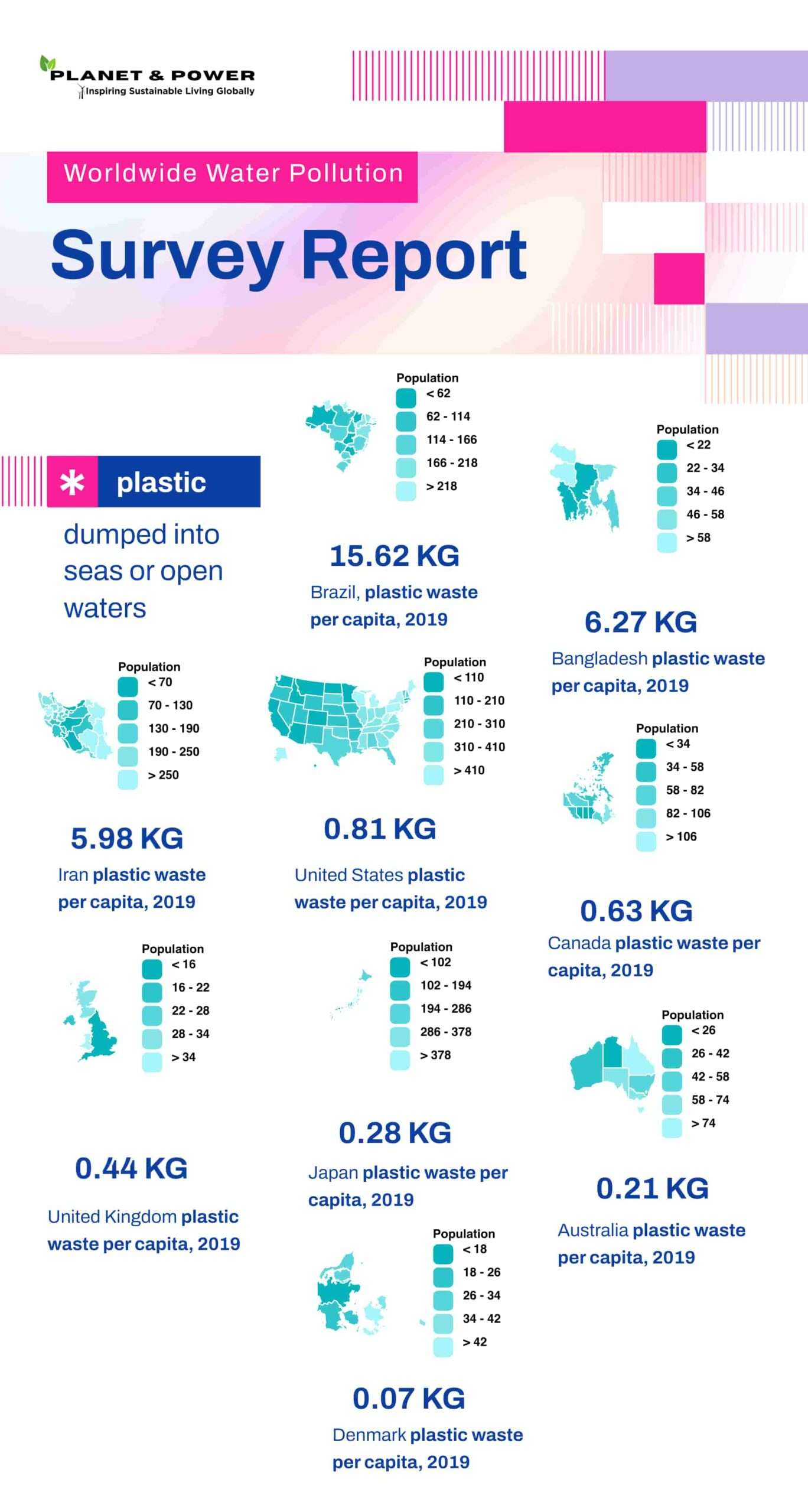
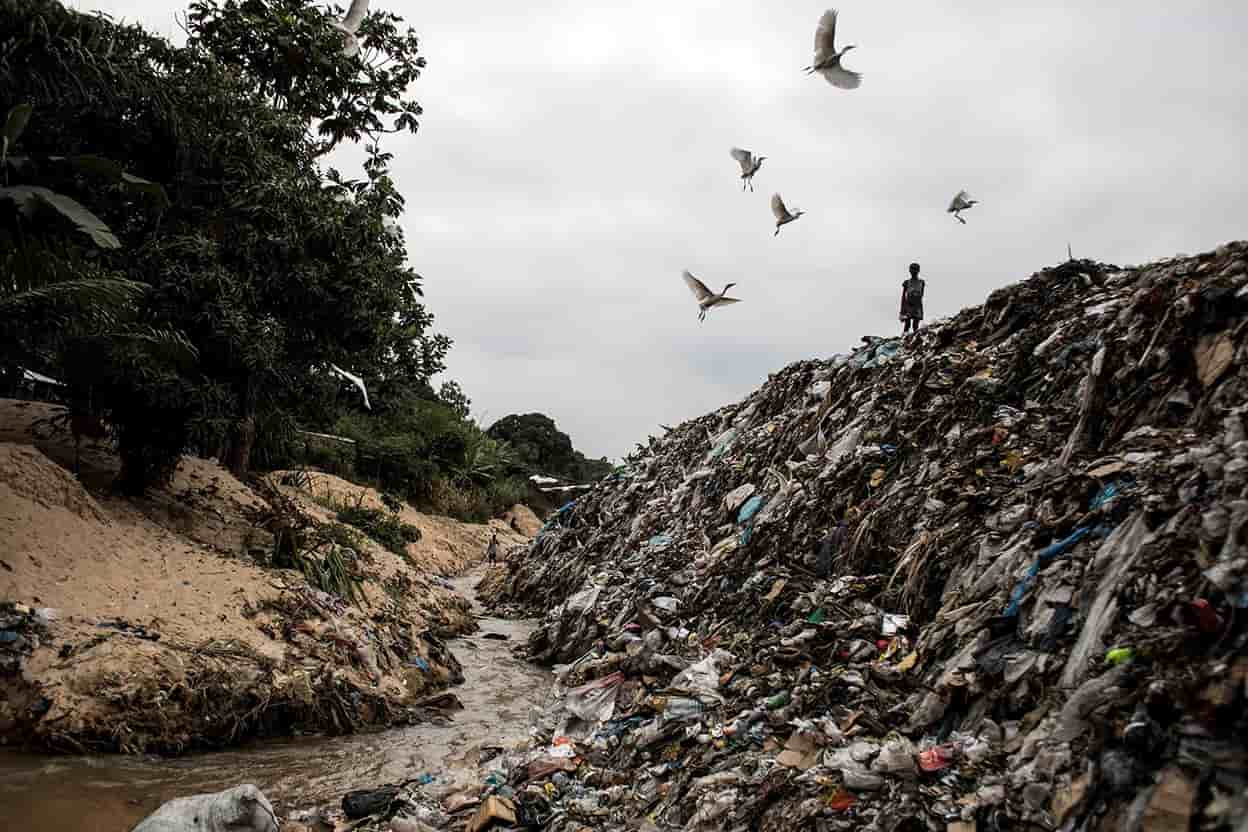
- Support Legislation for Cleaner Waterways – Every year, humans dump 300 million tons of plastic waste into rivers and oceans, polluting our environment and endangering marine life. Not only is plastic an environmental catastrophe but it also poses serious threats to ecosystems. Plastic pollution in rivers, seas, and oceans has become an ever-increasing problem, leading to waste islands and garbage spots forming over time. Recent events have only compounded plastic pollution problems, as disposable masks and gloves contributed to ever-increasing waste piles from the COVID-19 pandemic. However, modern technologies, innovative businesspeople, and startups are rising to meet this challenge of cleansing our water sources and protecting Earth’s ecology. In this article, we will investigate how dedicated individuals and organizations are revolutionizing water source cleaning to a whole new level. In 2015, experts conducted a detailed study on over 40,000 rivers flowing into the Pacific Ocean which yielded unexpected findings: almost all garbage entering oceans originates in rivers. Out of all of the rivers worldwide, only 20 rivers account for most of the plastic waste entering our oceans most are concentrated in Southeast Asia. Eighty percent of the garbage found in our oceans comes from just 1,000 of the dirtiest rivers worldwide – this represents approximately 2.7 million tons of plastic waste each year. Recognizing this problem led to an urgent search for solutions to stop garbage from entering oceans through rivers. Since 2013, a Dutch ocean cleanup startup led by inventor Boyan Slat has been working towards finding an answer to the ocean pollution crisis. Boyan and his team were awarded their initial grant of one hundred thousand dollars from PayPal founder Peter Thiel and launched their mission. Although facing numerous obstacles and harsh criticism, this project still managed to raise additional funds in 2019 – enough money for Boyan to create an autonomous vessel known as “The Interceptor.” The Interceptor was designed to catch garbage before it enters seas and oceans. The goal of The Ocean Cleanup Project is to equip polluted rivers worldwide with autonomous cleaning devices like The Interceptor for maximum pollution reduction. The Interceptor project’s first successful deployment took place in Jakarta, Indonesia before being installed in Malaysia, Vietnam’s Mekong Delta region, and Santo Domingo of the Dominican Republic. The Ocean Cleanup Project strives to collect up to 50 tons of garbage daily with each Interceptor vessel, creating an impactful way of reducing river and ocean pollution. Each vessel can fill 100 tons at one time and will run efficiently for 20 years. Costing approximately 780 thousand dollars, one vessel represents an investment of roughly 780,000 USD, but the project aims to cover some of its expenses by selling collected plastic waste. Pet ton cost approximately 800 dollars thus providing not only funding for the project but also creating economic incentives for local communities to join cleaning efforts.
- Investment in Water Treatment Technology – Recently, scientists have become increasingly concerned with the presence of “forever chemicals” in our water supply. Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) are among these chemicals you may encounter in everyday items like clothes, toothfloss, and toilet paper. Research estimates that up to 200 million Americans may be exposed to these chemicals through tap water however, there is hope on the horizon. Engineers have developed an innovative solution for treating and eliminating forever chemicals from water sources that could have profound impacts on both the environment and public health. Engineers developed two distinct strategies for extracting them: firstly they have created materials known as PFAS sorbents with the capacity to trap various forms of PFAS contaminants and secondly, they developed novel materials called biosorbents that capture more than 80 types of PFAS molecules at once. These sorbents outshone conventional treatment methods, making them an attractive solution for water treatment. Once saturated, captured chemicals can be concentrated into a solution that can then be destroyed through innovative techniques. This technological breakthrough marks an important advancement in the fight against toxic chemicals, by effectively eliminating and disposing of these toxic materials engineers can protect both public health and the environment. So much has already been accomplished. While further study and development may still be necessary, what has already been achieved is impressive. Chemicals present a serious threat to human health as well as water sources we consume.
Do We Have Time To Get Rid From Water Pollution?
From space, our planet appears more ocean than land. However, despite covering 71% of its surface area with water bodies, more than half of the global population experiences extreme water scarcity for at least one month each year. Estimates predict that by 2040, 20 additional countries could experience water shortages, leading to alarming statistics about our freshwater reserves being depleted. Unfortunately, both answers can be true at once. The water cycle never ceases to produce and recycle water, turning mist from liquid to ice as it travels around the planet. Thus, freshwater resources will never run dry, prompting one to wonder not how much is present, but whether access is available. On Earth, 97% of the liquid is salt water that cannot be consumed or used for agriculture. Of that remaining 3% that could potentially be utilized, most have frozen in ice caps and mountains – leaving less than one percent available to support life on our planet – rivers, lakes, underground aquifers, sea ice, permafrost and permafrost are among its locations. Humans are depleting these sources quickly, while rainfall and snowfall replenish them slowly but unevenly worldwide. As each region’s climate and geography vary significantly, some regions experience greater precipitation and water sources while other locations feature geographical features that make water transportation much more challenging. Farmlands often receive too much water, while still feeding those who depend on them. As of now, one-third of food that leaves farms ends up lost or wasted. Another option would be eating food that requires less water such as nuts or red meat becoming meatless might cut our water use by up to 30%.
The End of This Writing
The last thing we want to say is that we have tried to present the latest and true information to our readers. We do not know how much success we have achieved in writing this. Our readers’ responses will tell us how successful we are. The sole aim of our efforts was to prevent our readers from getting confused with all kinds of information about water pollution and to know the right information to prevent water pollution for the next generation.
Any valid sourceable information is possible to add. To add your opinion Contact Planet and Power