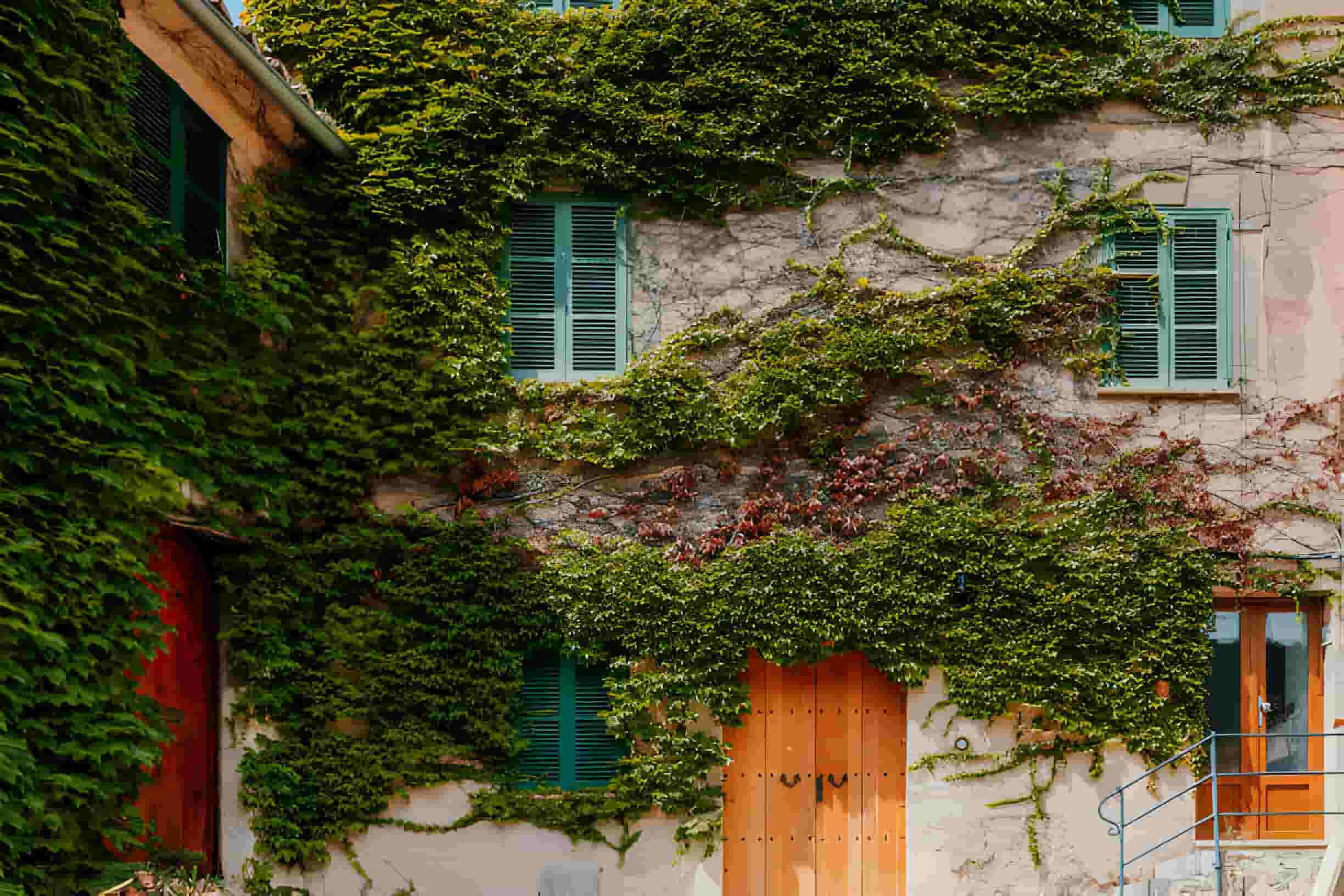
Designing with Nature is in short we can frame as the beauty of living building materials. The biological, polymer, and cement chemistry combo combine to create a sustainable material with unique properties. Bacteria and other microorganisms are used in the process to make the structure come alive.
Living building materials, biological building materials, or whatever name you prefer, these things are built with the help of microorganisms that play a very important role in manufacturing. The little organisms act as tiny factories that develop live-able material that can even multiply and heal cracks. It’s magical stuff.
Switching from our most commonly used building materials will save us from releasing greenhouse gases into the air like cement does. Construction projects have a significant impact on pollution due to their heavy use of cement which is a major source of industrial pollution. By replacing it with this mixture we can help combat pollution and reduce construction’s negative impact on our environment.

Inspiration Behind Living Building Materials
When it comes to developing living building materials, scientists often turn to nature for inspiration. For instance, the process of how organisms such as corals secrete limestone has birthed the idea of creating materials that can heal and grow. When you look at the coral reef, it’s formed by colonies of coral polyps which are held by calcium carbonate. This same model is being used to develop more self-sufficient building materials too.
Table of contents
Production of Living Building Materials
Bacteria isn’t just something that makes you sick. Researchers like Will Rube have been using it to create building blocks. They’ve found a type of bacteria called cyanobacteria that can make living building materials with sunlight and water. They use the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere along with sand and gelatin. The bacteria produces calcium carbonate, which binds with the sand, solidifying it into microcrete or bio cement. This is hard, living brick material that will last for quite sometime
The best way to describe living buildings is ‘mind-boggling.’ Did you know that living bricks can reproduce and grow into more bricks? It’s true. As long as they have enough resources and the right conditions, this phenomenon will happen. This exponential manufacturing allows for a sustainable, cheap alternative to traditional building materials. Thanks to this ability, we can make them at an insanely fast rate. On top of that, these materials can help protect us from the dangers of climate change.
We wanna talk about Self Healing Concrete
For years, concrete has been the go-to construction resource. It’s a strong material that holds up under all sorts of conditions. But it isn’t perfect. Cracks are one of the biggest problems with traditional concrete structures, and they can be extremely expensive to fix when they eventually occur. To address this issue and improve its other properties, researchers and engineers have been tinkering with the concept in recent years. The result is self-healing concrete, which could change how we build our infrastructure from highways to homes and everything in between.
Understanding Self-Healing Concrete Concrete that heals itself? Sounds like something from a science fiction movie, but it’s real and it’s here. It’s called self-healing concrete and it’s a freak of nature, just like you. Not only does this type of material have the ability to repair any cracks or damage on its own, but it can also withstand anything life throws at it without batting an eye. What kind of sorcery did they use to create such a thing? Well, they used biological agents such as bacteria to fill in cracks and make the material stronger. Imagine if we could do that with our bones. When engineers incorporate these properties into concrete structures, they’ll be able to sit back and relax for years knowing their creations are more resilient than them. Suddenly I’m looking at contractors in an entirely new light.
The Science Behind Self-Healing Concrete Can you imagine a concrete that can heal itself? That’s right. Thanks to nature and its mysteries, we now have self-healing concrete. In nature, organisms like bacteria can repair themselves when they’re damaged. So why not concrete too, you know?
When traditional concrete cracks or gets damaged in any way, it’s usually a huge pain to repair and it’s so costly. Self-healing concrete has special bacteria embedded within the material during production. It stays dormant until cracks appear and then it becomes alive and starts producing calcium carbonate which fills in the cracks. Not only does this kind of technology help reduce the costs of maintenance, but it also helps with energy conservation and reducing waste as well. Making it environmentally friendly for construction projects is always a plus.
Applications of Self-Healing Concrete The applications for self-healing concrete are many and vast. Think of the construction industry, from building foundations to roadways and bridges. Integrating self-healing properties into concrete can lead to buildings that will be able to withstand environmental factors and wear and tear. A technology like this could transform how infrastructure is designed and built in the future, making it more durable while saving costs. Engineers daily experiment with new ways to improve self-healing concrete so that it can become practical for real-world use. With constant developments in material science and technology, there’s no doubt that when it comes to sustainable construction this will be an important component in the future.
Building Industry with Grass-Based Materials
A start-up in the US has thrown a curveball at the building industry by inventing new and improved ways of making building materials. Using plants that grow quickly, it has managed to make materials that capture more carbon than trees do. This new way of doing things is not only sustainable but also eco-friendly. Benefits of Grass-Based Materials These grass-based materials have benefits. They’re environmentally friendly and are perfect for the construction industry. They bind fibers of grass together through some secret method and they’re tough as nails. Very fitting for constructing homes, buildings, and infrastructure.
- Carbon Capture: The grass used in these materials can capture more carbon than trees, helping to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change.
- Biodegradable: The materials are biodegradable, reducing waste and conserving resources, making them a sustainable solution for the building industry.
- Rapid Growth: The grasses used in this process grow quickly, allowing for large quantities to be harvested efficiently.

The Future of Grass-Based Materials
Grass-based materials might soon be a standard in the construction industry. There’s a huge demand for eco-friendly building supplies these days, and this material could be the answer. With its one-of-a-kind properties and sustainability benefits, grass-based is capable of tackling our climate emergency quickly. Not only that but they also aid in lowering carbon emissions and encourage sustainable practices.

By incorporating grass-based materials into construction projects, builders and developers can contribute to a greener and more environmentally conscious future. The use of these materials not only helps to combat climate change but also showcases the possibilities of innovative approaches to sustainable construction. As the industry continues to embrace eco-friendly alternatives, the adoption of grass-based materials is poised to make a significant impact on the way buildings are constructed and the environmental footprint of the construction sector.
Overall Fact checking for Green Living Building Materials in 2024
Green living materials are natural earth-sourced products that help protect our planet. When it comes to construction, these green materials are the way to go. They are both recycled and reusable which in turn grants them access to benefits like thermal efficiency and safety. By creating an eco-efficient home with sustainable architecture you can also lower energy bills while reducing the cost of home insurance policies.
Trending Green Living Building Materials in 2024
- Cobb – Cobb is one of the oldest organic building materials, made of subsoil, water, and fibrous organic materials like straw, and sometimes lime. It acts as a natural insulator, saving energy and keeping homes cool in hot climates.
- Stone – Stone buildings are low maintenance, environmentally friendly, and toxin-free. They are durable, easy to clean, and work well in different climates, making them a sustainable choice for construction.
- Recycled Plastic – Concrete made from recycled plastic reduces greenhouse gas emissions and gives plastic waste a new purpose. Recycled plastic can also be used to create various building materials like polymeric timbers, cables, pipes, and flooring.
- Steel – Steel is a highly recyclable building material that is used to reinforce structures and create durable homes. Homes with steel frames are cost-effective, durable, and environmentally friendly.
- Precast Concrete Slabs – Precast concrete slabs are energy-efficient, chemical-free, and produce minimal waste. They are ideal for walls, building facades, floors, and roofs, providing a cost-effective and environmentally friendly building material option.
- Recycled Glass – Recycled glass countertops transform recycled glass into distinctive kitchen surfaces. This sustainable material reduces waste, energy consumption, and landfill usage, making it an eco-friendly choice for homes.
- Hempcrete – Hempcrete is a lightweight and environmentally friendly building material made from hemp fibers, sand, and lime. It is pest and fire-resistant, acts as a good insulator, and is a renewable resource, making it an excellent choice for sustainable construction.
- LED Lighting – LED bulbs are energy-efficient, long-lasting, and environmentally friendly. Switching to LED lighting can significantly reduce energy consumption and carbon footprint, making it a sustainable lighting option for homes.
- Cork – Cork is an excellent insulator for homes, helping to maintain stable indoor temperatures. It is lightweight, environmentally friendly, and resistant to mold and mildew, making it a sustainable insulation material.
- Adobe Brick – Adobe bricks, made from clay and straw, are a traditional and environmentally friendly building material. They help maintain stable indoor temperatures, reduce sound transmission, and are easy to modify for creative architectural designs.
Advancements in technology and the use of green building materials are helping humans live more sustainably and protect our planet. By choosing eco-friendly materials for construction, we can reduce our carbon footprint, conserve energy, and create healthier living environments for future generations.
Advances in Living Building Materials
The construction industry is evolving at an alarming rate. The building materials we thought we knew have been abandoned for new-age innovations that are truly defying the limits of what we can do. From concrete that heals itself to structures that are printed in 3D, the future of construction is an exciting place. Let’s take a look at some of the most groundbreaking advancements in building materials and see firsthand how they’re changing the game for everyone involved.

- Living Walls – Bringing Nature Back Concrete doesn’t have to be the enemy of greenery – living walls and verdant tapestries are climbing the sides of buildings, bringing nature back to the urban landscape. These living ecosystems filter air, reduce noise pollution, and provide habitats for birds and insects.
- Concrete – The Living Guardian of Our Cities The days are gone when concrete was thought of as heavy and fragile. At present, self-healing fibers, nanomaterials, and carbon-capturing additives have been embedded in it. Imagine how tall buildings can repair tiny fractures before they degenerate into big problems or bridges that decontaminate the atmosphere while standing still. Concrete’s future is resilient and sustainable, it will always be a breathing, vibrant caretaker of our urban areas.
- Steel – The Silent Sentinel Thus, steel, the pillar of contemporary buildings, is changing. The high-performance alloys are not only light but also make it possible for slim and audacious structures to rise high above all. It’s more about weight though- some steels even contain sensors that can measure stress and strain hence averting a complete collapse. Beyond that, this new kind of steel is something more than material it is a live sentry ensuring our safety as well.
- Composites – The Harmony of Nature and Technology Composites, the marriage of natural and synthetic materials, are creating a new melody of strength and sustainability. Imagine bamboo woven into beams or flax woven into car panels – these biobased composites are the harmony of nature and technology, singing a song of a greener future.
- 3D Printing – Shattering Traditional Construction The construction industry is experiencing a revolution due to the advent of three-dimensional printing. 3D printing is changing the face of traditional construction by allowing for elaborate and tailored structures that are created layer by layer. 3D printing is opening up new horizons in terms of what can be achieved through conventional construction techniques, such as overnight homes or bridges that defy gravity using delicate latticeworks.
- Self-Healing Wonders – Building Resilience The era of holes and fractures in the walls will soon be a bygone issue thanks to these self-healing materials. The lifespan of structures is now being elongated and waste reduced through such materials as bacteria-added concrete that fills cracks or polymers with microcapsules used for mending damage.
- Biomimicry – Learning from Nature Design efficiency and biomimicry are some of nature’s many lessons. It is an art that man has come to know as nature impersonation where structures inspired by honeycombs are being built, and lotus leaf surfaces are being made, all of which make structures blend with the environment and reduce ecological footprints.
- Transparent Revolution – Smart Glass Glass is not just a clear substance anymore – smart glass can turn opaque by the flicking of a switch. Think about what it would be like to have facades that change with the sun’s movements, absorbing heat and reflections while flooding rooms with sunlight. This technology has made living and working in glass buildings different from before.
- Kinetic Canvas – Dynamic Structures They are not still objects anymore – they have become moving buildings that are responsive to the environment, as exemplified by the way such structures sway and dance with the wind and thus optimize natural ventilation while capturing sunlight. They follow the rhythm of a city and this makes them energy efficient (building façades that change to optimize energy use) or able to absorb vibrations (bridges).
- Material Intelligence – Building with Brains Materials embedded with sensors provide data to smart systems that make structures that can adapt to weather conditions and avoid being destroyed. Can you imagine frontages that give priority to the uses of energy or bridges that monitor their health is how buildings will look in the future where materials blend with machinery?
- Sustainable Symphony – Eco-Conscious Materials A symphony of eco-concerns is being played by the sustainable materials born from recycling and renewable sources as well. From mycelium-based structures to plastic roads, these materials attest to a future in which construction shall only leave its trace on the earth through whispers.
- Collaborative Canvas – Open-Source Materials It is not compulsory for innovation to be kept in a laboratory, open-source materials are making construction more democratic in the future. Communities can use local materials to build houses of their choice and a variety of designers can post online recipes of those things, connecting the world in co-creation.
- The Future of Construction – Construction’s future is a kaleidoscope of imaginative material wonders. There are no limits to the potential for self-cleaning facades and buildings that produce their energy.
- Bridging the Gap – Materials are better than ever as they face the challenge of dominating any type of nature. For example, by putting solar panels on roads or embedding self-cooling membranes on buildings, human beings are now able to live even in parts of the earth that could not be imagined before such as deserts and tundra.
- The Human Touch – Buildings are more than just structures – they are about connection and inspiration. Materials imbued with a human touch, from interactive paint to kinetic sculptures, are fostering emotional resonance and interaction in our built environment.
Remember, the future of construction is being built one groundbreaking material at a time. Subscribe to this channel to delve deeper into these material marvels and witness the rise of a world where buildings are more than just shelter – they are living testaments to human ingenuity.
Living Building Challenge Red List
Have you heard of the Living Building Challenge and products compliant with the Living Building Challenge Red List? If not, don’t worry – Our team from the Planet and Power sustainability team is here to break it down for you.

A green building standard by the name of the Living Building Challenge has come up. If you think LEED is strict, then this one’s gonna blow your mind While LEED has a mix of requirements that can be picked to reach a certain level of certification, The Living Building Challenge requires all standards in it to be met. That’s right, every single one. You might wanna prepare yourself because this isn’t going to be an easy task. When it comes to focusing on sustainability and such, The Living Building Challenge does not play. It makes use of renewable energy (net zero energy) and treats all water on-site as two examples among many others. These requirements are made with the intention of “pushing” buildings to be more sustainable and eco-friendly.
Compliance with the Living Building Challenge Red List Herman Miller offers products that are compliant with the Living Building Challenge Red List. This means that these products meet the specific requirements outlined in the challenge to ensure they are environmentally friendly and safe for use in sustainable building projects.
If you are working on a project that requires Living Building Challenge compliance, contact the Herman Miller sustainability team to get a list of products that meet these requirements. When dealing with systems and similar products, which may require further steps to guarantee compliance, never overlook the minutest details.
How to Learn More If you want to dive deeper into the Living Building Challenge and understand the specific requirements and elements of the standard, you can reach out to the sustainability team for more information. Additionally, there are resources available online where you can explore the protocol and learn more about what it takes to achieve Living Building Challenge compliance.
Living Building Challenge materials
The Living Building Challenge remains unique in the sustainable architecture and design world as a robust comprehensive guidance for producing buildings that are not just green, but also healing and regenerative. The heart of this challenge is seven major petals forming the basis of its principles which aid architects and designers to construct structures that are genuinely alive within their surroundings.
- Understanding Place The initial petal of The Living Building Challenge entails learning the specific locality where construction works will take place in the future. The first thing is that it involves understanding the climate, topography, and natural features of the place to minimize the negative impacts of the building on its environment. When an architect designs a building with concern for the site, such as an edifice is going to be at home in nature rather than taking against it.
- Responsible Energy and Water Use Responsible use of energy and water is the theme for the second and third petals. When all energy needed in a building is generated on-site, while all water is captured and treated there, this can greatly minimize damage to the environment through buildings. This focus on self-sufficiency plus effectiveness raises the bar for sustainability in our built environment.
- Eliminating Harmful Materials The 4th petal of The Living Building Challenge is dedicated to the use of materials. It concentrates on eradicating chemicals and materials that are known to pose a risk to human health and the environment. Designers can create buildings that foster a healthier planet for all life, by selecting building components that are not poisonous, energy efficient, or sustainably sourced.
- Criteria for Well-Being The Living Building Challenge goes beyond the fundamental concepts of sustainability through a set of various other criteria that relate to human welfare and social equality. These criteria include happiness and well-being, equity, and biophilic design which aim at creating spaces that not only perform their intended functions but also improve life quality for their inhabitants. By stressing the link between people and their larger ecology, this challenge fosters a more comprehensive design.
Further Insights
Inspiring our readers to make sense of the visual feeling of Solar-Powered, Net Zero Water: Amazing “Living” Building Tour by R.W. Kern Center.
Another tour of Beyond Path
We are at the end of part
In today’s world, where energy consumption and environmental impact are major concerns, researchers are exploring the possibilities of smart materials to revolutionize the way we build and interact with our surroundings. Imagine a world where buildings can adapt to changing environmental conditions, reducing energy consumption and material waste. This vision is becoming a reality through the development of innovative materials that have the potential to transform the way we think about architecture. Wouldn’t it be wonderful if materials were capable of more than one thing? What if the door was also the screen of a computer? What if walls could control the climate of a room without the need for external heating or cooling systems? These are the questions that researchers in the field of smart materials are asking. Ultimately, our goal of this research is to create a greener future where buildings and technologies can coexist in balance with the natural world. The dream of sustainable materials that can revolutionize the way we build and interact with our environment is within reach, thanks to the dedication and collaboration of researchers in the field of smart materials.