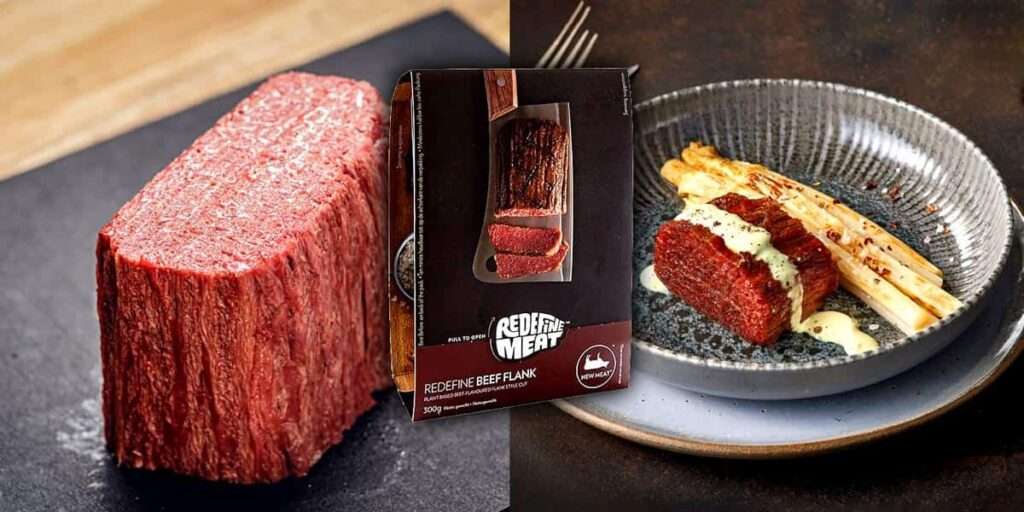
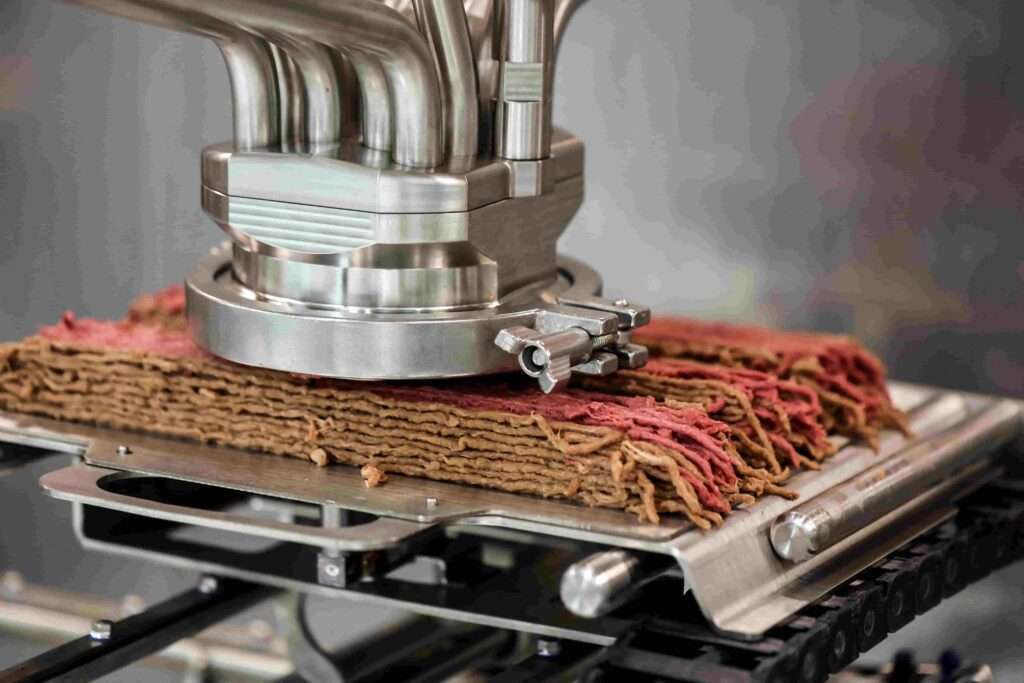
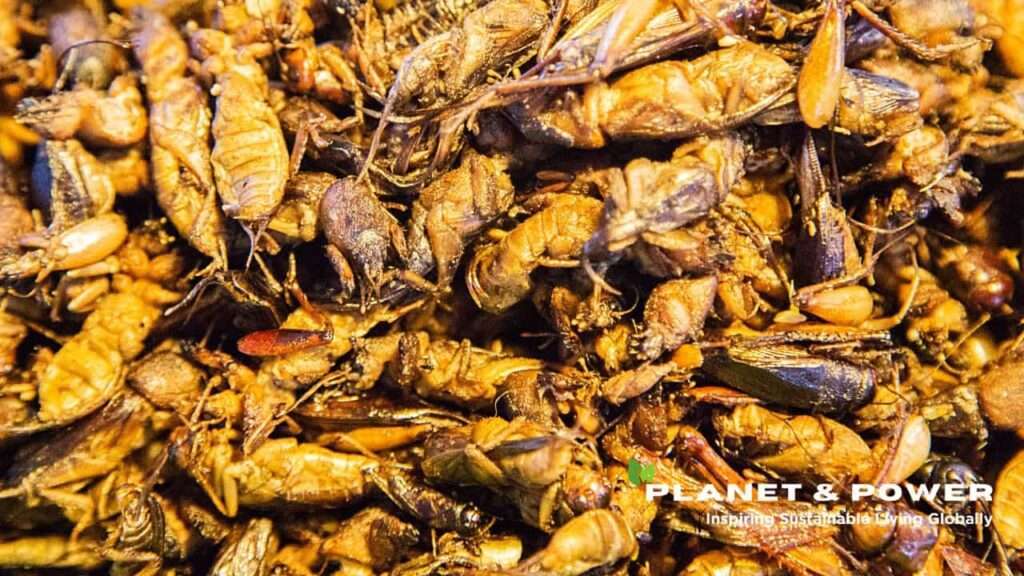
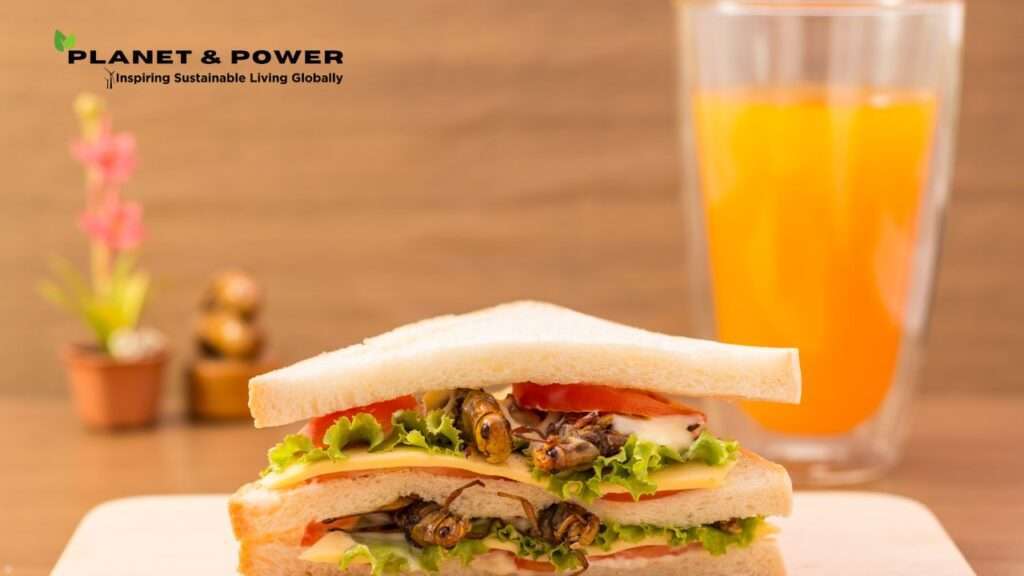
Magnesium is a crucial mineral that our bodies need for many different functions. This element is found in large amounts in our bodies and is very important for our health. While most people think of it as just a nutrient, its significance goes even further than we realize.
Magnesium is essential for:
- Energy Production: Mg is important for our bodies because it helps turn food into energy. It is important for cells to have this element because ATP is their main source of energy.
- Protein Synthesis: Magnesium plays a crucial role in the body by assisting in the process of turning amino acids into proteins. This is important for building and repairing muscles.
- Neurological Function: It’s extremely important for keeping our nerves functioning properly. Magnesium plays a key role in controlling the neurotransmitters that communicate messages in our brain and nervous system.
- DNA Synthesis: Magnesium plays a crucial role in helping our bodies create and maintain DNA and RNA, which are essential for proper cell function. It also helps activate over 300 different enzymes that are needed for various bodily processes.
- Muscle Contraction and Relaxation: It helps muscle contractions work smoothly by teaming up with calcium, allowing muscles to both relax and contract efficiently.
- Blood Glucose Control: Magnesium is important for regulating blood sugar levels and helping with insulin sensitivity.
- Cardiovascular Health: Magnesium is crucial for keeping our hearts healthy. It plays a key role in controlling our heartbeat and promoting good blood flow by keeping our arteries relaxed and open.
Newly released studies have highlighted the significant impact of not getting enough magnesium in our diets. Researchers have found links between low magnesium levels and various health problems, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, brittle bones, and severe headaches.To keep our health and well-being in good shape, we need to make sure we get enough magnesium.
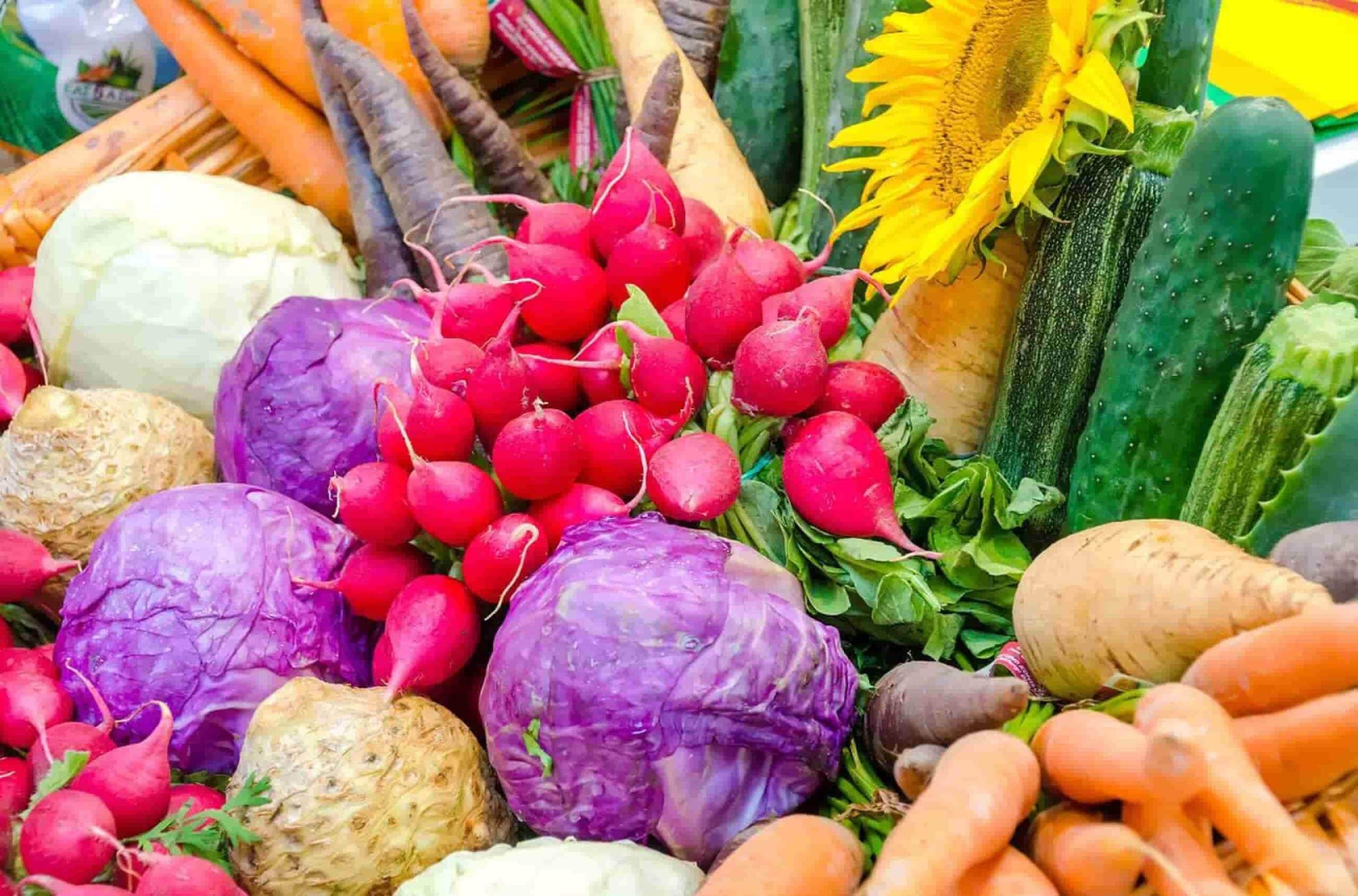

Dietary sources of magnesium include:
- Green Leafy Vegetables: Such as spinach and kale.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, cashews, and pumpkin seeds.
- Legumes: Like black beans and lentils.
- Whole Grains: Including brown rice and oatmeal.
- Fish: Such as salmon and mackerel.
- Dairy Products: Like yogurt and milk.
Table of contents
Uses of Magnesium Over Time
Different cultures have used magnesium for a very long time.. It is valued for its flexibility and easy availability, and people have found many practical uses for it over the years.
Ancient Uses
- Medicinal: The ancient Greeks and Romans used minerals containing magnesium for medicinal reasons, which helped them deal with problems like digestive issues and skin conditions.
- Construction: The ancient Egyptian architects who built the pyramids used dolomite, a type of magnesium carbonate found in nature, in their construction materials.
Middle Ages
- Alchemy: In the Middle Ages, alchemists used to call magnesium compounds “magnesia alba” and were fascinated by their mysterious properties.
- Agriculture: Farmers found that by adding magnesium to the soil, they were able to increase their crop yields. This discovery led to the early use of magnesium in agriculture.
18th and 19th Centuries
- Discovery of Element: In 1755, the Scottish chemist Joseph Black discovered that magnesium was an element, which helped us learn more about its chemical characteristics.
- Industrial Uses: In the 19th century, people started using magnesium in different industries like photography, pyrotechnics, and early electrical engineering. It was an important material for all these fields.
20th Century
- World War Applications: During both World Wars, magnesium’s light weight and strength made it highly sought after for military uses, especially in making airplanes and incendiary weapons.
- Health Supplements: As scientists delved deeper into research, they began to uncover the numerous health benefits of magnesium. This finally led to the creation of magnesium supplements to help people who might not be getting enough magnesium.
Modern Day
- Aerospace and Automotive: At the moment, magnesium alloys are very important in the aerospace and car industries. The main goal is to cut down on weight to make the car use less gas and perform better overall.
- Medicine: Magnesium has become a common ingredient in medical treatments, like Epsom salts for soothing muscles and magnesium sulfate for treating preeclampsia during pregnancy.
Technology: The technology industry finds magnesium’s ability to conduct electricity beneficial in electronics and portable devices.
Magnesium and Bone Health: Evidence from Studies
Many studies have looked into how magnesium affects bone health, and they have found that magnesium is important for building strong bones. If you don’t get enough magnesium, you could get osteoporosis or other bone problems. What have researchers found in these studies? Let’s take a better look.
Clinical Studies and Findings
- Magnesium Intake and Bone Density: Several studies have shown that higher magnesium intake correlates with increased bone density. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research reported that women with higher dietary magnesium intake had a significantly lower risk of hip fractures.
- Supplementation Studies: Participants with osteoporosis were given magnesium supplements in a study, and after six months, there was a significant increase in bone mineral density. This study demonstrated the potential of magnesium as a helpful treatment for osteoporosis.
Observational Studies
- Population-Based Studies: According to data from the Framingham Heart Study, individuals with lower magnesium levels often had reduced bone mass and greater incidences of fractures compared to those with higher magnesium levels.
- Longitudinal Research: During a study that lasted for a long time and looked at how diet affects bone health, scientists discovered that people who consistently ate enough magnesium had much fewer bone problems over the course of ten years.
Expert Opinions
A number of experts are in consensus about how crucial magnesium is for keeping our bones healthy. According to Dr. John Seamen, who specializes in endocrinology, magnesium is just as important as calcium when it comes to bone health. It plays a key role in enzymatic reactions within the bone matrix, which is essential for keeping our bones strong.
Veganism and Its Environmental Claims
Veganism is a way of life that involves avoiding the consumption of animal products and also refraining from supporting any form of animal exploitation or mistreatment. Most of the time, people choose to live a vegan lifestyle because they care about the world.
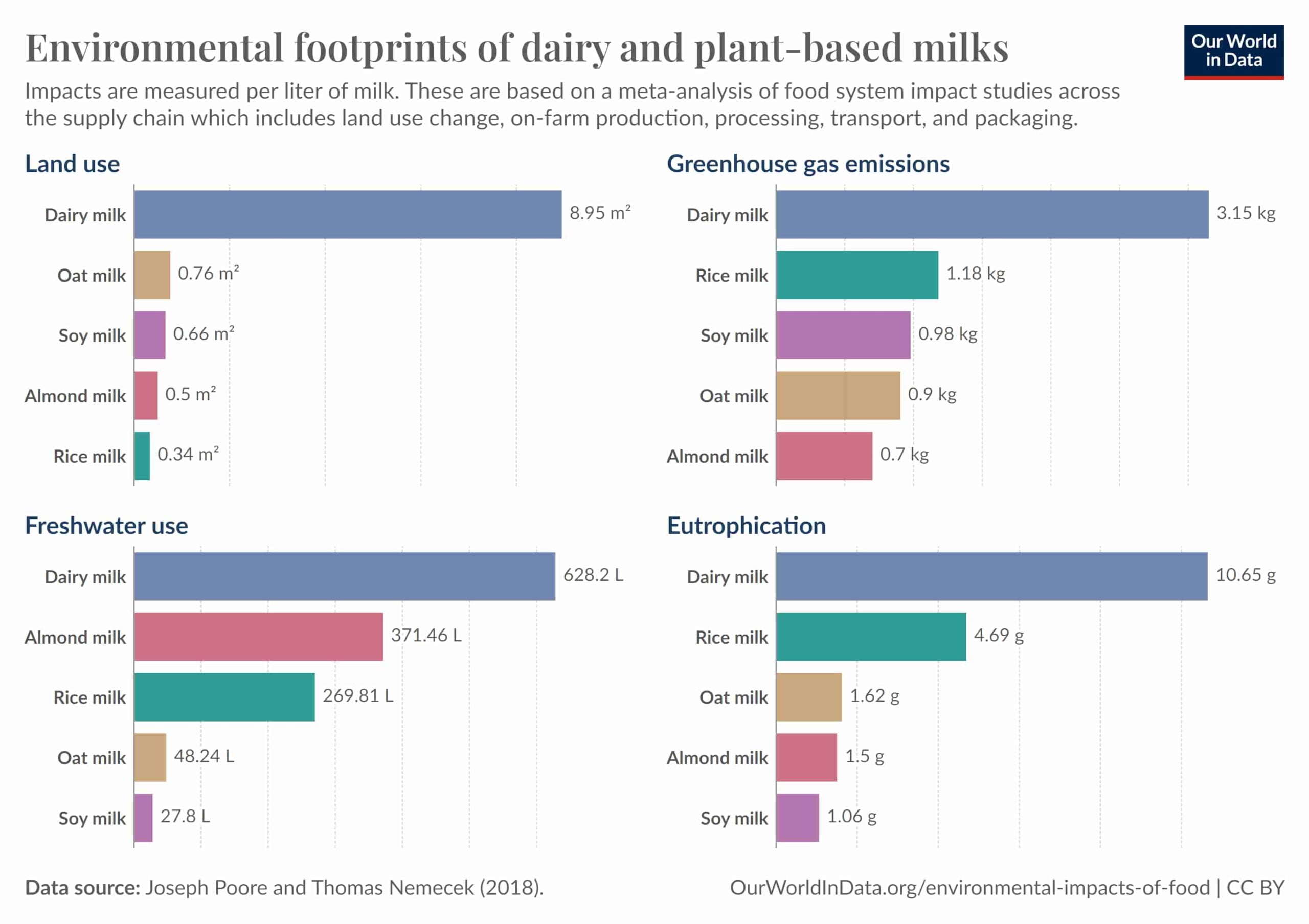
- Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Raising animals for food production releases large amounts of methane and nitrous oxide, which are powerful contributors to climate change.
- Conservation of Water Resources: Many liters of water are needed to grow the food that animals eat and for the animals to drink.
- Decreased Land Use: Raising animals and growing feed crops requires a lot more land than growing plants for food.
Biodiversity Preservation: Decreasing the amount of livestock farming can help lessen the impact of habitat destruction and deforestation.
Effects of Animal Farming on the Environment
Animal farming has big effects on the world in many ways, including:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A lot of methane and nitrous oxide are released when livestock are raised. These are both strong climate gases.
- Deforestation: Huge sections of forests are being cut down to make room for grazing animals or to grow crops for animal feed. This is causing wildlife to lose their homes and is also leading to a decrease in the variety of plant and animal species in those areas.
- Water Usage: Raising animals for food uses up a lot of water, between growing feed for them and giving them water to drink.
- Pollution: The animal waste and chemical fertilizers that are used in making animal feed are causing contamination in the air and water.
Energy Consumption: The process of producing feed, housing animals, and slaughtering them uses a lot of energy, which ultimately harms the environment.
Plant-Based Diets: Benefits and Drawbacks
Plant-based diets can have numerous benefits, including:
- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions
- Lower water consumption
- Decreased land use
- Improved health outcomes, such as lower risks of heart disease

However, there are drawbacks to consider:
- Nutrient deficiencies, particularly in Vitamin B12 and iron
- Potential overreliance on processed vegan foods
- Higher costs associated with specialty vegan products
Eating a plant-based diet can have a big impact on both the environment and your health. To make sure you get all the nutrients you need, though, you should plan your meals ahead of time. The availability of plant-based food options can also vary depending on where you live, which can affect how easy it is to stick to this kind of diet.
Vegan vs. Omnivorous Lifestyles
When analyzing carbon footprints, dietary choices significantly impact environmental outcomes.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Vegan diets generally produce fewer emissions.
- Omnivorous diets contribute more due to livestock farming.
- Land Use
- Vegan diets require less land.
- Meat production necessitates extensive pastures and feed crop land.
- Water Use
- Plant-based diets often result in lower water consumption.
- Animal farming demands vast amounts of water for both animals and feed crops.
- Energy Consumption
- Vegan diets typically consume less energy.
- Animal products require significant energy inputs for processing and transportation.
Economic and Social Implications of Veganism
Economic and social implications of veganism are multifaceted.
- Market Growth: The vegan market has grown a lot, which has opened up new business possibilities.
- Job Creation: Increased demand for plant-based products has generated new jobs within the agriculture and food industry.
- Economic Displacement: Traditional animal farming sectors face economic strain and potential job losses.
Socially, veganism promotes:
- Health Awareness: Talking more about health benefits makes people more likely to eat healthy foods.
- Ethical Considerations: Enhanced awareness of animal welfare issues influences societal values.
Cultural Shifts: Growing acceptance and normalization of plant-based diets impact cultural traditions and practices.
Is Going Vegan a Sustainable Choice?
Going vegan encompasses numerous elements.
- Environmental Impact: Numerous studies show that eating more plant-based foods can significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduce the amount of land needed for agriculture, and decrease water consumption when compared to diets that are high in animal products.
- Biodiversity: Decreasing the practice of animal farming can play a key role in saving our ecosystems and safeguarding endangered species from losing their homes due to habitat destruction.
- Resource Efficiency: Growing plants for people to eat is typically more efficient than raising animals for meat and dairy because animals need a lot of food.
- Health Benefits: When you carefully plan a vegan diet, it can help improve your health, and this could also be good for the environment by lessening the burden on healthcare systems.

In the end, making big changes to our lifestyle and the way we do agriculture is crucial. We need to focus on providing education that covers all sides of the issue and helping people make informed choices.