In recent years, there has been a growing interest in incorporating insects into our diets. People are beginning to realize the many benefits that insects can offer as a food source. From being nutrient-dense to environmentally friendly, insects are becoming a staple in many cultures around the world.
The most popular insects to consume are the mealworm and Entomophagy. With their high protein content and versatility in cooking, these insects are gaining popularity as a sustainable and nutritious food option.
The Nutritional Value of Insects Insects are often referred to as superfoods due to their high nutrient density. They are packed with essential vitamins and minerals, making them a valuable addition to any diet. Insects offer a unique combination of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates that are essential for our overall health and well-being.
And also insects are a sustainable source of protein, requiring significantly fewer resources to produce compared to traditional livestock. They are also more efficient at converting feed into food, making them an attractive option for feeding a growing population.
The Role of Insects in the Food System Insects are a crucial component of the food system, especially in light of environmental challenges such as biodiversity loss and climate change. By embracing insects as a sustainable food source, we can help reduce the strain on the environment and promote a more balanced and resilient food system.
While there may be cultural barriers to overcome, the benefits of incorporating insects into our diet are undeniable. With advancements in technology and a growing interest in alternative protein sources, insects are poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of food production and consumption.
What is Entomophagy?
Entomophagy, derived from the Greek words “entomon” meaning insect, and “phagein” meaning to eat, refers to the practice of consuming insects. While initially, the focus was on promoting the consumption of insects for their nutritional benefits, the individual shifted the narrative towards exploring the broader impact of entomophagy on society. By delving into the history, cultural practices, and sustainability aspects of eating insects, the individual aimed to change perceptions and foster a deeper understanding of this practice.

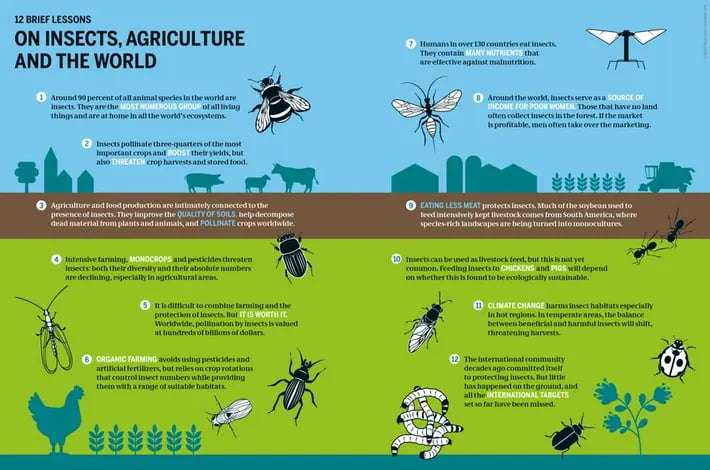
A Historical Perspective Since prehistoric times, humans have been consuming insects as a source of protein. From beetles to grasshoppers, the practice of eating insects dates back to the era of hunter-gatherers. Cave paintings depicting humans consuming insects offer a glimpse into our ancestral dietary habits. Despite entomophagy losing popularity with the rise of agriculture and livestock farming, over 2 billion people across 80% of countries worldwide continue to incorporate insects into their diets.
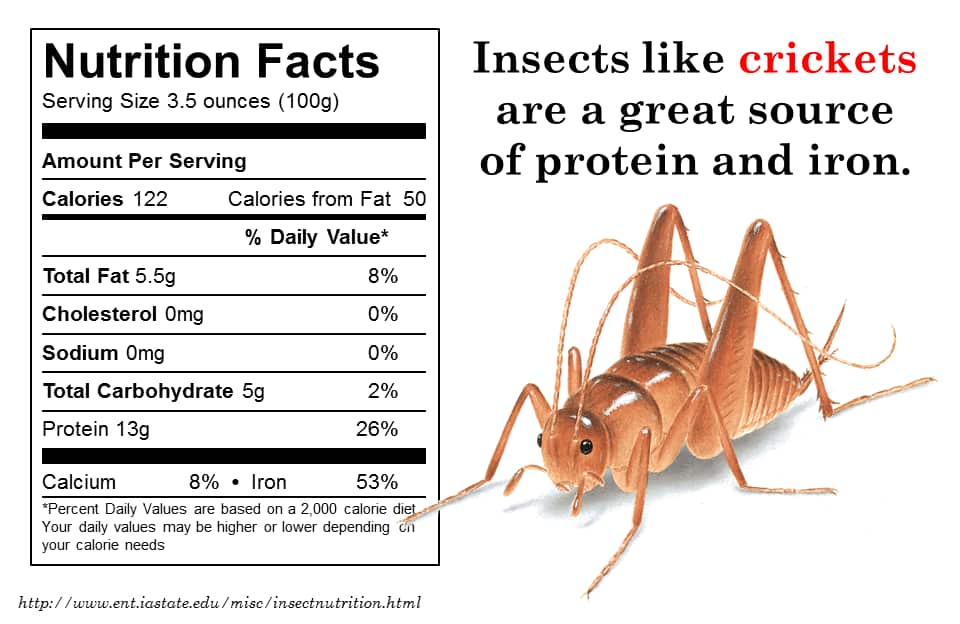
Nutritional Benefits Aside from their sustainability advantages, insects are also packed with essential nutrients. High in protein, fiber, and micronutrients, insects offer a nutritious alternative to conventional meats. With up to 80% protein content and lower fat levels compared to beef, insects present a viable option for meeting dietary requirements while reducing environmental impact. Contrary to common misconceptions, insects are packed with essential nutrients, making them a valuable source of protein.
As we find out, there are over 2,000 edible insect species, each offering varying amounts of nutrition. By incorporating insects into their diets, individuals can access a diverse range of nutrient sources that are incredibly dense. Whether it’s mealworms, chaplains, crickets, or locusts, there is a wide variety of edible insects to choose from, each with its unique nutritional profile.
Cultural Exchange Through Cuisine Exploring entomophagy opens doors to understanding diverse culinary traditions and cultural practices. From fried tarantulas in Cambodia to toasted grasshoppers in Mexico, insect-based dishes offer a window into the rich tapestry of global cuisine. By embracing unfamiliar foods and customs, we nurture a spirit of curiosity and appreciation for the cultural diversity that enriches our world.
Animal protein has long been a staple in the North American diet, but as resources become scarcer and populations continue to grow. And yes, the search for sustainable protein sources is becoming increasingly important. Insects are emerging as a new superfood that offers a viable solution to these challenges.
Insect Consumption Around the World In many parts of the world, insect consumption is not just a novelty but a common and even delicious part of daily diets. Countries like Thailand and China have embraced insects as edible foods, with some insect species even considered delicacies. Not only do insects offer a sustainable source of protein, but they also provide a variety of flavors and textures depending on the species and how they are cooked.
The Rise of Edible Insects in North America In North America, the idea of eating insects has often been met with skepticism, but a group of Canadian students from McGill University is working to change that. In 2013, they won $1 million to launch Aspire Food Group, a company focused on farming insects to address global food insecurity. Through innovative approaches and partnerships, Aspire Food Group aims to make insect farming a sustainable and accessible solution to protein deficiency in underserved communities.
The Environmental Benefits of Insect Farming Feeding insects as a protein source can have significant environmental advantages compared to traditional livestock production. Insects require less land, water, and feed to produce the same amount of protein, making them a more resource-efficient option. With meat production contributing to a significant portion of greenhouse gas emissions, the shift towards insect farming could help reduce the environmental impact of food production.
Promoting a Sustainable Future As the global population continues to grow and resources become increasingly strained, the need for sustainable protein sources becomes more urgent. Insects offer a nutritious and resource-efficient alternative to traditional livestock, making them a key player in the future of food security. By promoting entomophagy, or the consumption of insects by humans, we can work towards a more sustainable and equitable food system.
What do Doctors say about eating insects?
Check out the video,
What science reports about eating Entomophagy
With over 80% of the world’s countries already incorporating insects into their diets, it’s evident that entomophagy, or the practice of eating insects, is not a new concept. In fact, over 2 billion people consume bugs as a common food ingredient every day. However, in Western cultures, the idea of eating insects may seem unusual. As the global population is projected to reach 9 billion by 2050, the food industry faces the challenge of increasing food production while minimizing its environmental impact.

Traditional livestock production is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, ranging from 11 to 17%. In light of the climate crisis, there is a growing interest in alternative and more sustainable protein sources. Insects, such as crickets (Wikipedia), have emerged as a viable and eco-friendly option due to their low resource requirements for growth and production.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact As the world grapples with the implications of climate change, it’s essential to prioritize sustainable food production practices. Insects offer a compelling solution to the challenges posed by traditional livestock farming. Insects require significantly less water, land, and feed compared to conventional livestock, making them a more environmentally friendly protein source.
By shifting towards insect-based foods, anyone can play a role in reducing the food industry’s carbon footprint and promoting sustainable consumption practices. Embracing insects as a food source not only benefits the environment but also contributes to a more resilient and diversified food system.
Diversifying Protein Sources for the Future As the demand for protein continues to rise, it’s crucial to explore alternative protein sources that are sustainable and nutritious. Insects have the potential to play a significant role in diversifying the protein options available to consumers. While traditional protein sources like beef, pork, and chicken may not be sustainable on a large scale, insects offer a viable alternative that is both environmentally friendly and nutritious. On the other hand innovations in lab-grown meat and plant-based alternatives, insects represent a promising protein source that can help address the challenges of food security and sustainability.

In Essence
The adoption of insects as a sustainable protein source holds great potential for addressing the global food security and environmental challenges we face. While the idea of eating insects may seem unconventional to some, it’s important to recognize the nutritional and environmental benefits that insects offer. By exploring new protein sources like insects, we can pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient food future. As we embrace the diversity of edible insects and innovative food products, we take a step towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious food system.
Happy Reading 🙂