Definition and Importance of Solar Parks
A solar park is good for the earth because the energy it produces is abundant and can be used over and over again. The sun’s energy is always being made, unlike fossil fuels, which are limited and take hundreds of years to refill. This makes it truly renewable. While drilling for oil and gas changes the environment and ecosystems, solar parks are generally built on top of buildings that are already there or on land that isn’t being used, like landfills, parking lots, or roofs. This keeps natural areas safe and causes less damage to the environment. Also, the production process at the solar park doesn’t use any pollutants or toxins, so the air we breathe and the water we drink are safer.
Table of contents
Estimated reading time: 0 minutes
Current Trends in Solar Park Development
As we witness the successful transmission of solar energy from space to Earth, and the creation of the world’s first solar-powered train, it’s clear that the future of solar power is brighter than ever before. See this video,
Feasibility Study and Site Selection
In any project, doing a feasibility study is crucial to see if a site is viable and suitable. This study looks at factors like resource availability, market demand, and financial impacts. Site selection involves evaluating various options based on the project’s needs and goals. It ensures the chosen site aligns with the project’s objectives and maximizes its chances for success.
Factors Influencing Site Selection: There are several factors that influence the selection of a site for a project. These include:
- Geographic Location: The geographic location of a site plays a significant role in determining its suitability. Factors such as proximity to transportation networks, customer base, and suppliers, as well as access to resources, can impact the overall success of a project. A favorable geographic location can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve market reach.
- Solar Irradiance: Solar irradiance refers to the amount of solar energy a specific location receives. Areas with high solar irradiance are more conducive to solar power generation, as they can produce more electricity.
- Land Availability and Use: The availability of suitable land is essential for various projects, such as industrial facilities, commercial buildings, or renewable energy installations. Factors like land size, ownership, zoning regulations, and land use restrictions need to be considered during site selection.
- Environmental and Social Impact Assessments: Environmental impact assessments evaluate potential effects on air, water, soil, and biodiversity. Social impact assessments analyze the project’s influence on local communities, cultural heritage, and social dynamics. These assessments help identify and mitigate any adverse effects, ensuring responsible project development.
- Economic Viability and Return on Investment: Economic viability and ROI are crucial for any project. To assess financial feasibility, you need to look at capital investment, operating costs, revenue potential, and payback period. ROI analysis shows if the project is profitable and sustainable in the long run. A positive ROI means the project can generate good returns and provide a favorable financial outcome.
Design and Layout of Solar Parks
Designing and laying out solar parks requires careful consideration to maximize energy production and efficiency. Factors such as site characteristics, available space, and environmental impact need to be taken into account. To gain insights into solar park design and layout, Planet and Power analyzed various resources and websites.
Types of Solar Panels
Monocrystalline
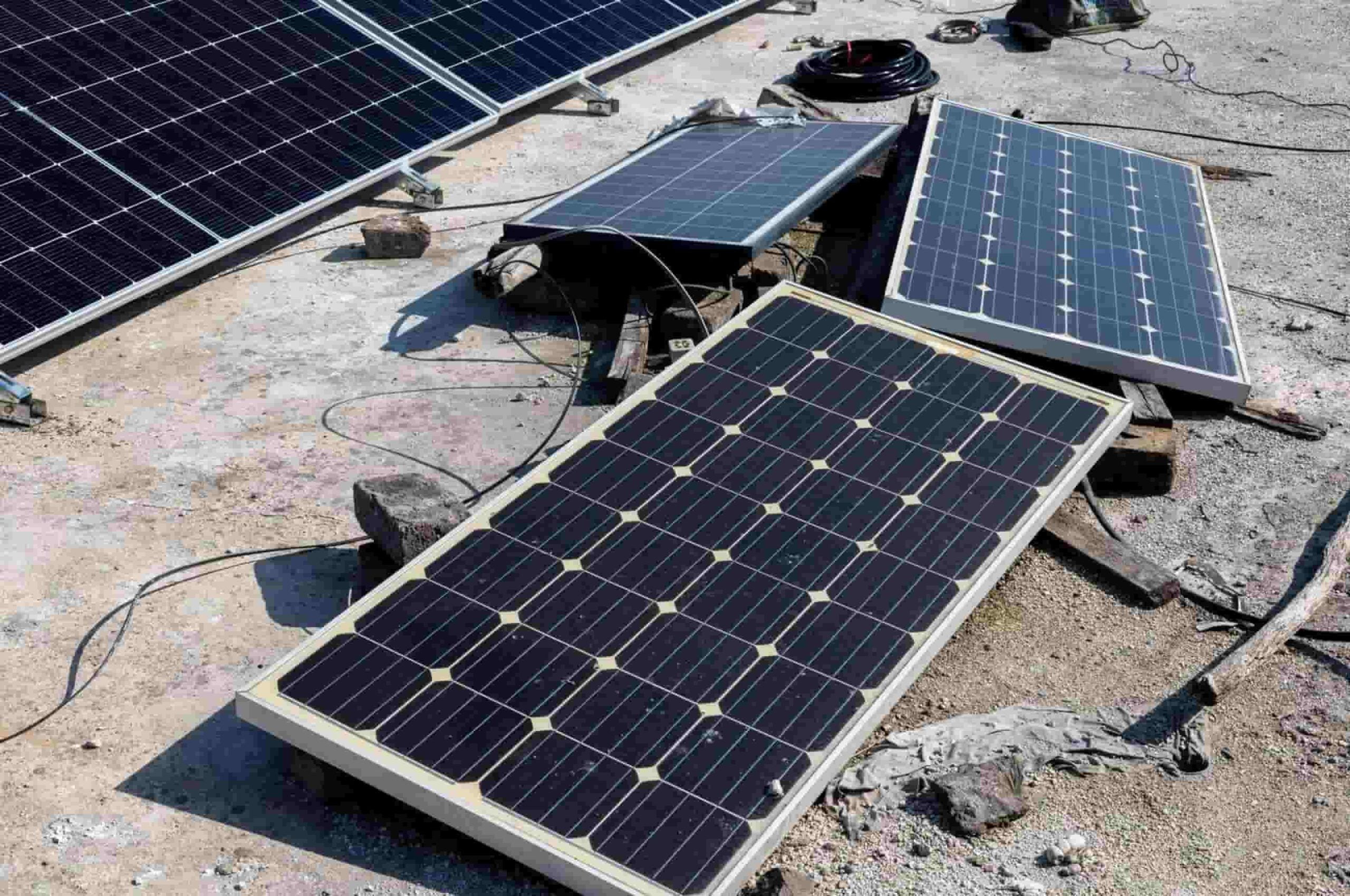

Polycrystalline
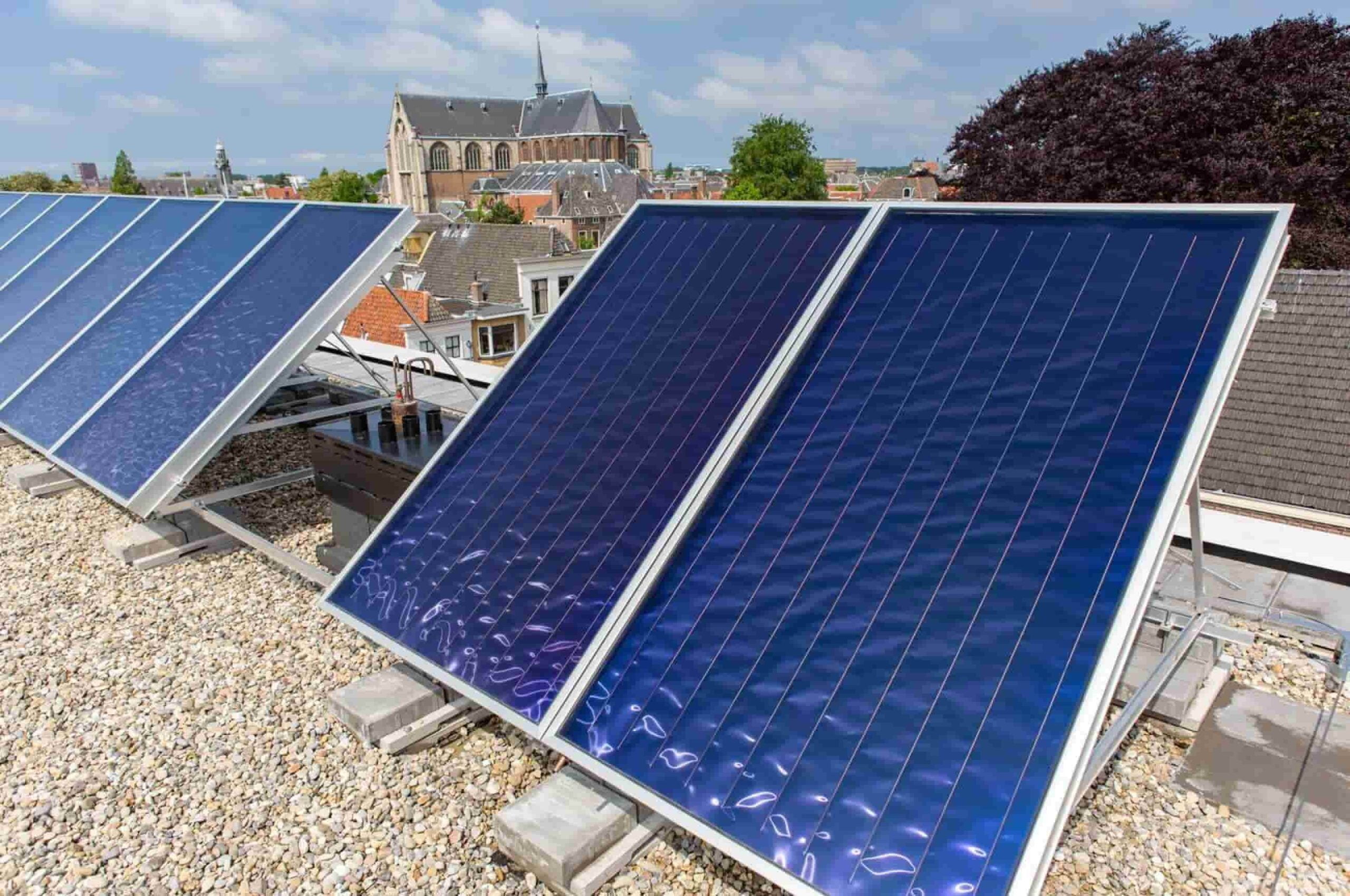

Thin-Film
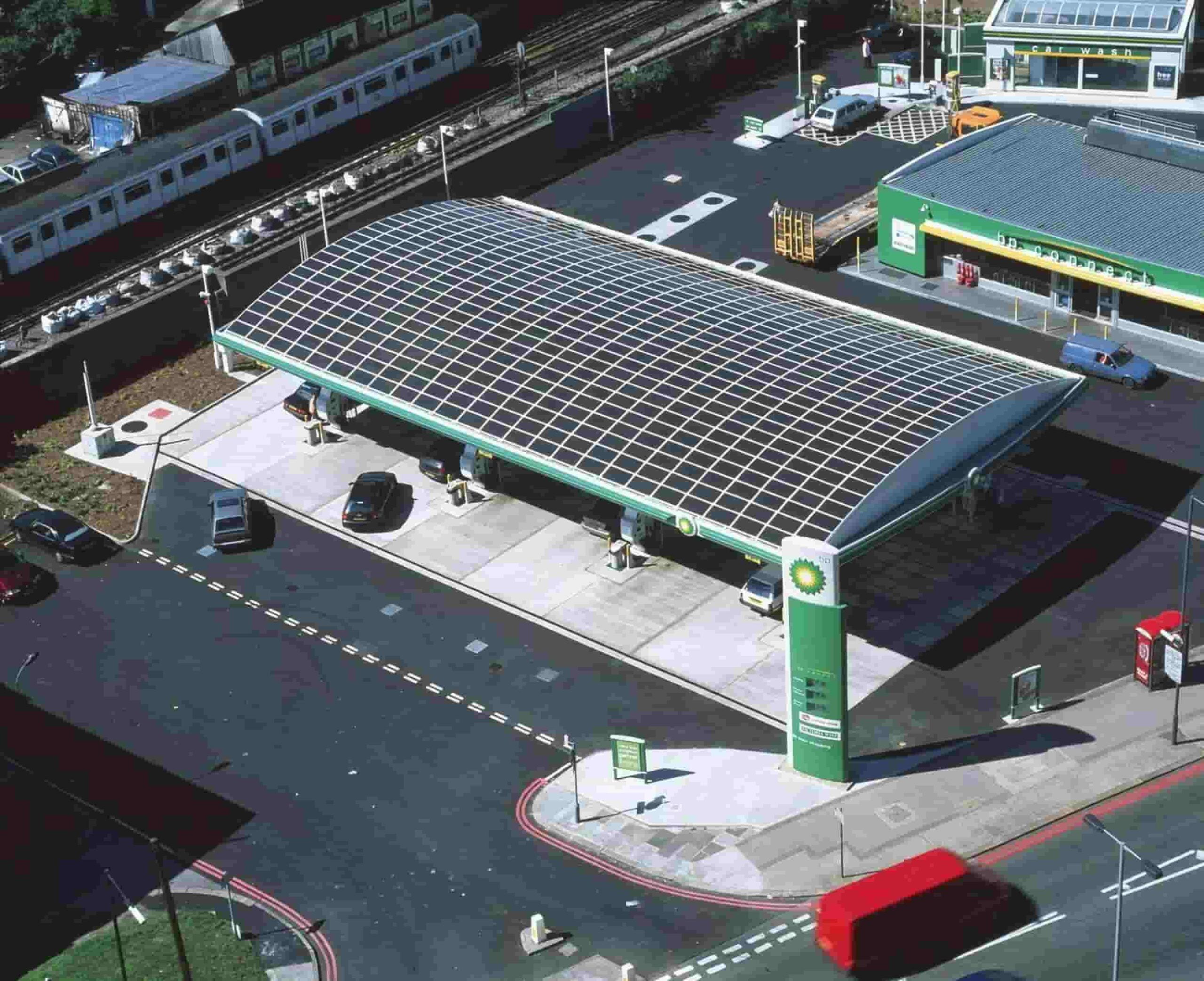

Mounting Systems – Fixed vs. Tracking Systems The choice between fixed and tracking mounting systems for solar panels depends on various factors such as energy output goals, available space, and budget.
Optimal Layout for Maximum Efficiency – One key factor in a solar park’s layout is arranging the panels to avoid shading and capture maximum sunlight. Proper spacing and orientation are crucial. By spacing the panels well, each one gets plenty of sunlight without being shaded by its neighbor. Also, angling the panels just right to face the sun boosts energy production. The park’s overall layout matters too, like how rows are arranged and where inverters and other equipment are positioned. These details all add up to a more efficient solar park.
Team of Planet and Power Solar Energy are doing constant research about Latest updates on Design and Pre construction elements for a Solar Park. We will continuously update the post here.